Configure SASE Internet Protection Rules
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
Internet protection rules are firewall rules that are applied to internet-bound traffic on a per-tenant basis. They provide network protection by establishing match criteria and enforcement actions. To configure internet protection rules, you configure the following match criteria and enforcement actions, as described in this article.
- Applications and URLs—Match criteria based on individual applications, groups of applications, categories of applications, predefined URL categories (such as business and economy, computer and internet security, and entertainment and arts), and predefined reputations (such as high and low risk).
- Users and user groups—Match criteria based on individual users or groups of users.
- Source geolocation and source IP address—Match criteria based on the geographic location of source or destination traffic.
- Network Layer 3 and Layer 4—Match criteria based on the IP address of the source and destination traffic or on custom or predefined protocol-based services.
- Security enforcement—After you select the match conditions, you specify a security enforcement action, which is either allow, deny, or reject. You can also create custom security enforcement profiles in which you specify the enforcement criteria.
- Review and deploy—After you have configured match criteria and security enforcement actions, you review and then deploy the internet protection rule.
Note: You must configure the SASE rules, profiles, and settings in the following order:
- Configure users and user groups first, and then publish them to the gateway. For more information, see Configure SASE Users and Groups.
- Configure site-to-site tunnels. For more information, see Configure SASE Site-to-Site Tunnels.
- Configure secure client access profiles and rules. For more information, see Configure SASE Secure Client Access Rules.
You do not need to configure the remaining SASE rules, profiles, and settings in any particular order.
When you begin to configure your first internet protection policy, the following screen displays to guide you through the procedure:

To configure internet protection rule match criteria:
- Go to Configure > Real-Time Protection > Internet Protection.

The following screen displays.

The Internet Protection Rules List screen displays all configured internet protection rules, including built-in rules. Built-in rules are predefined in Concerto and behave the same as other user-defined rules. They are automatically generated when you publish a tenant, but they are disabled. If you enable a built-in rule, you can modify, reorder, move, and delete it. If you delete a built-in rule and then republish the tenant, the rule is created again. Also, if you edit the name of a built-in rule and then publish, the version of the rule with the revised name is retained, and the original built-in rule is generated again. To use a built-in rule, SASE needs to be enabled on the tenant and the tenant needs to have VSIA solution tier.
Note: Release 12.2.1 supports the new built-in GenAI_Firewall internet protection rule. It is linked to one DLP filtering profile (GenAI_DLP) and one URL filtering profile (GenAI_Firewall).
- In the horizontal menu bar, you can select one of the following operations.

Operation Description Add Create a new internet protection rule. This button is active when no existing rule is selected. Clone Clone the selected internet protection rule. When you select this option, the configuration wizard for the rule displays with the Review & Deploy screen selected. You can rename the default name of the cloned rule, if needed, and then click Save.
Reorder Reorder the selected internet protection rule. A popup window similar to the following displays.

1. Select the rule order:
- Process the rule last.
- Process the rule first.
- Process the rule in specific placement—A list of the existing rules displays. Click the position in the list where you want to place the rule.
2. Click Move.
Delete Delete the selected internet protection rule. A popup window similar to the following displays:

Click Yes to delete the internet protection rule, or click No to retain the rule.
Refresh Refresh the list of existing rules. - To customize which columns display, click Select Columns and then click the columns to display or hide. Click Reset to return to the default column settings.
The options are:- Applications & URLs
- Users & Groups
- Device Groups
- Endpoint Posture
- Source & Destination
- Services
- Schedule
- Source
- Destination
- Security Enforcement
- Status
- Creation Date
- Last Modified
- Proceed to the next section to configure application and URL-filtering match criteria.
Configure SASE Application and URL Filtering for Internet Protection Rules
You create application and URL filters to prevent access to specific applications and URLs, thus allowing you to control web-browsing activity within an organization. Uncontrolled access to internet websites can expose an organization to security risks, such as threat propagation, loss of data, and lack of compliance.
Application identification provides an effective detection capability for evasive applications such as Facebook, Skype, Torrent, and WhatsApp. It identifies applications and protocols at different network layers based on the protocol bundle rather than using the IP address and port number. You can create custom application and URL categories on a per-tenant basis. You can associate a reputation value with the URL category. Each custom URL category has a unique name and defines information about the URLs to match using a string match or a pattern match. For information about creating custom applications and application groups, see Configure SASE User-Defined Objects.
To configure application and URL-filtering match criteria:
- In the Internet Protection Rules List screen, click + Add to create a rule. The Create Internet Protection Rule screen displays, with Step 1, Applications, selected. By default, all applications, URLs, and reputations are matched by this rule. To accept the default settings, click Next to continue to Step 2, Users & Groups.

Note: You can include only certain application groups, applications, or application categories in the match list. The screen displays all custom and predefined application groups. Note that you can create internet protection rules based on either applications or URL categories and reputations, but not both. To match both applications and URL categories or reputations, create two separate internet protection rules. Click Add New to add a new application category. See the Configure Application Categories section in Configure SASE User-Defined Objects.
Add New to add a new application category. See the Configure Application Categories section in Configure SASE User-Defined Objects.
- To create an internet protection rule based on application groups, select the user-defined and/or predefined application groups to include in the match list, or type the name of the application group in the search box and select it from the search results. The application group is added to the search bar. In the following example, the custom application group AppGroup1 and the predefined application groups Adobe-Apps and Box-Apps are selected. To remove an application, click X next to the application in the search box.
Click the Information icon next to each application group or application category to see the tags associated with the application group or category.
Information icon next to each application group or application category to see the tags associated with the application group or category.
To create a new application group, click Add New. See Configure Cloud Applications To Use with API-Based Data Protection.
Add New. See Configure Cloud Applications To Use with API-Based Data Protection.

- Click the Applications tab in the submenu. The following screen displays.

- Select the custom and predefined applications to include in the match list, or type the name of the application in the search box and then select it from the search results. The application is added to the search bar. To remove an application, click X next to the application in the search box.
Note: In Release 12.2.1 and later deprecated predefined applications are not displayed. If you had already configured a rule in Releases 12.1.1 and earlier that included a now-deprecated application in its match criteria, and then try to edit that rule, an error message similar to the following is displayed.

- Click the Application Category tab in the submenu. The following screen displays.

- Select the user-defined and/or predefined application categories to include in the match list, or type the name of the application category in the search box and then select it from the search results. The application category is added to the search bar. To remove an application category, click X next to the application category in the search box.
- To create an internet protection rule based on URL categories and reputations, click the URL Categories & Reputations tab in the top menu. The following screen displays.
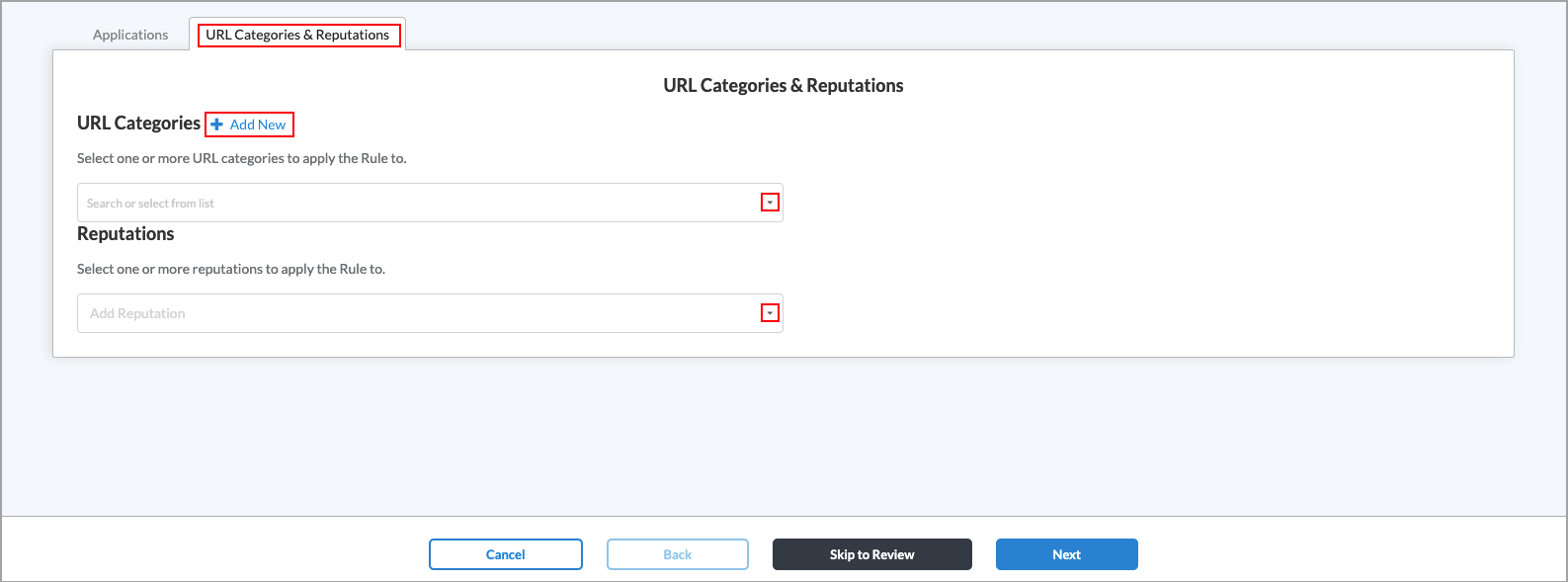
- In the URL Categories and Reputation fields, select one or more URL categories and reputations to include in the internet protection rule. The URL category and reputation are added to the respective search bar. To remove a URL category or reputation, click X next to the name in the search box.
The following table lists the predefined URL categories that are currently supported.
Category Name Description Abortion
Abortion topics, either prolife or prochoice. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://abortion.procon.org, http://www.nafcanada.org.
Abused Drugs
Discussion or remedies for illegal, illicit, or other commonly abused drugs such as heroin, cocaine, and other street drugs. Information about legal highs, including glue sniffing, misuse of prescription drugs, and abuse of other legal substances. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://shroomery.org, http://passyourdrugtest.com.
Adult and Pornography
Sexually explicit material for the purpose of arousing a sexual or prurient interest. Adult products including sex toys, CD-ROMs, and videos. Online groups, including newsgroups and forums, that are sexually explicit in nature. Erotic stories and textual descriptions of sexual acts. Adult services including videoconferencing, escort services, and strip clubs. Sexually explicit art. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://playboy.com, http://union.fr.
Alcohol and Tobacco
Sites that provide information about, promote, or support the sale of alcoholic beverages or tobacco products and associated paraphernalia. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://thompsoncigar.com, http://wineinsiders.com.
Auctions
Sites that support the offering and purchasing of goods between individuals as their main purpose. Does not include classified advertisements. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://ebay.com, http://quibids.com.
Bot Nets
URLs, typically IP addresses, that are determined to be part of a bot network, from which network attacks are launched. Attacks may include spam messages, denial of service (DoS), SQL injections, proxy jacking, and other unsolicited contacts.
Business and Economy
Business firms, corporate websites, business information, economics, marketing, management, and entrepreneurship. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://samsung.com, http://ups.com.
cdns Delivery of content and data for third parties, including ads, media, files, images, and video. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://metacdn.com, http://edgestream.com. Cheating
Sites that support cheating and plagiarism and that contain related materials, including free essays, and exam copies. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://essaymania.com, http://echeat.com.
Computer and Internet Info
General computer and internet sites, and technical information. SaaS sites and other URLs that deliver internet services. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://ranking.com, http://system.netsuite.com.
Computer and Internet Security
Computer security and internet security, and security discussion groups. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://siteadvisor.com, http://webroot.com.
Confirmed spam sources URLs from which large volumes of spam originates. Cult and Occult
Methods, means of instruction, or other resources to interpret, affect, or influence real events through the use of astrology, spells, curses, magic powers, satanic or supernatural beings. Includes horoscope sites. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://horoscopes.com, http://astronet.hu.
Dating
Dating websites focused on establishing personal relationships. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://eharmony.com, http://christianmingle.com.
Dead Sites
Sites that do not respond to http queries. Policy engines should usually treat these as uncategorized sites. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://g00gle.com, http://whitehouse.info.
DNS over HTTPS Known DNS Over HTTPs (DoH) providers and domains. Examples of websites that fall into this category: https://cloudflare-dns.com and https://doh.opendns.com. Dynamic Content
Domains that generate content dynamically based on arguments to their URLs or other information (such as geolocation) on incoming web requests.
Educational Institutions
Preschool, elementary, secondary, high school, college, university, and vocational schools and other educational content and information, including enrollment, tuition, and syllabi. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://mit.edu, http://ucsd.edu, http://www.carlsbadusd.k12.ca.us/.
Entertainment and Arts
Motion pictures, videos, television, music and programming guides, books, comics, movie theaters, galleries, artists, or reviews about entertainment. Performing arts, such as theater, vaudeville, opera, and symphonies. Museums, galleries, and art or artist sites, such as sculpture and photography. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://eonline.com, http://highlightgallery.com.
Fashion and Beauty
Fashion or glamour magazines, beauty, clothes, cosmetics, style. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://visionmodels.co.uk/, http://genejuarez.com.
Financial Services
Banking services and other types of financial information, such as loans, accountancy, actuaries, banks, mortgages, and general insurance companies. Does not include sites that offer market information, or brokerage or trading services. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://firstpremierbankcards.com, http://paypal.com.
Food and Dining Food and dining sites. Gambling
Gambling or lottery web sites that invite the use of real or virtual money. Information or advice for placing wagers, participating in lotteries, gambling, or running numbers. Virtual casinos and offshore gambling ventures. Sports picks and betting pools. Virtual sports and fantasy leagues that offer large rewards or request significant wagers. Note that hotel and resort sites that do not enable gambling on the site are categorized in Travel or Local Information. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://www.powerball.com/pb_home.asp, http://www.zjlottery.com.
Games
Game playing or downloading, video games, computer games, electronic games, tips, and advice about games or how to obtain cheat codes. Sites dedicated to selling board games, andjournals and magazines dedicated to game playing. sites that support or host online sweepstakes and giveaways. Fantasy sports sites that also host games or game playing. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://duowan.com, http://ubi.com.
Generative AI Artificial intelligence tools and systems that are used to generate new text, images, video, audio, code, or other types of synthetic data. Examples of websites that fall into this category: https://bard.google.com and https://chat.openai.com/chat. Government
Information about government, government agencies, and government services such as taxation, public services, and emergency services. Sites that discuss or explain laws of various governmental entities. Local, county, state, and national government sites. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://www.nasa.gov, http://premier-ministre.gouv.fr.
Gross
Vomit and other bodily functions, bloody clothing, and so forth. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://ratemyvomit.com, http://bloody-disgusting.com.
Hacking
Illegal or questionable access to or use of communications equipment or software. Development and distribution of programs that may allow compromising of networks and systems. Avoidance of licensing and fees for computer programs and other systems. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://hackplayers.com, http://hackforums.net.
Hate and Racism
Sites that contain content and language in support of hate crimes and racism such as Nazi, neo-Nazi, and Ku Klux Klan. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://nazi-lauck-nsdapao.com/, http://americannaziparty.com/, http://kkk.com/.
Health and Medicine
General health, fitness, and well-being, including traditional and non-traditional methods and topics. Medical information about ailments and various conditions, dentistry, psychiatry, optometry, and other specialties. Hospitals and medical offices. Medical insurance. Cosmetic surgery. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://webmd.com, http://missionvalleymedical.com.
Home and Garden
Home issues and products, including maintenance, home safety, decor, cooking, gardening, home electronics, and design. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://homedepot.com, http://waysidegardens.com.
Hunting and Fishing
Sport hunting, gun clubs, and fishing. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://fishingworks.com, http://wildlifelicense.com.
Illegal
Criminal activity, how not to get caught, copyright and intellectual property violations. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://newid.com, http://kidneykidney.com.
Image and Video Search
Photo and image searches, online photo albums and digital photo exchange, image hosting. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://images.google.fr, http://gettyimages.com.
Individual Stock Advice and Tools
Promotion and facilitation of securities trading and management of investment assets. Information about financial investment strategies, quotes, and news. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://stockstar.com, http://morningstar.com.
Internet Communications
Internet telephony, messaging, VoIP services and related businesses. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://skype.com, http://www.chatib.com/.
Internet Portals
Web sites that aggregate a broader set of internet content and topics and that typically serve as the starting point for an end user. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://yahoo.com, http://qq.com.
Invalid URLs that do not meet the required format or contain invalid characters. Job Search
Assistance in finding employment, tools for locating prospective employers, or employers looking for employees. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://monster.com, http://51job.com.
Keyloggers and Monitoring
Downloads and discussion about software agents that track a user's keystrokes or monitor their web surfing habits. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://keylogger.org, http://spy-tools-directory.com.
Kids
Sites designed specifically for children and teenagers. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://www.mundogaturro.com, http://www.ri-ra.ie/.
Legal
Legal websites, law firms, discussions and analysis of legal issues. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://www.pepperlaw.com, http://earlcaterlaw.com.
Local Information
City guides and tourist information, including restaurants, area and regional information, and local points of interest. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://downtownlittlerock.com, http://sandiegorestaurants.com.
Low-THC Cannabis Products Sites with content about low-THC, non-psychoactive products, including CBD oils, resin, extracts, herbs, capsules, supplements, foods, drinks, and toiletries/skin care products. Examples of websites that fall into this category: https://alwayspureorganics.com and https://directhemp.com. Malware Sites
Malicious content, including executables, drive-by infection sites, malicious scripts, viruses, trojans, and code. For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Malware".
Marijuana
Marijuana use, cultivation, history, culture, legal issues. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://howtogrowmarijuana.com, http://cannaweed.com.
Military
Information about military branches, armed services, and military history. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://defense.gov, http://goarmy.com.
Motor Vehicles
Car reviews, vehicle purchasing or sales tips, parts catalogs. Auto trading, photos, discussion about vehicles including motorcycles, boats, cars, trucks and RVs. Journals and magazines about vehicle modifications. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://www.carmax.com, http://trade-a-plane.com.
Music
Music sales, distribution, streaming, information about musical groups and performances, lyrics, and the music business. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://itunes.com, http://bandcamp.com.
News and Media
Current events or contemporary issues of the day. Radio stations and magazines, newspapers online, headline news sites, news wire services, personalized news services, and weather sites. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://abcnews.go.com, http://newsoftheworld.co.uk.
Nudity
Nude or seminude depictions of the human body. These depictions are not necessarily sexual in intent or effect, but may include sites containing nude paintings or photo galleries of artistic nature. Nudist or naturist sites that contain pictures of nude individuals. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://gorod.tomsk.ru/index-1221486260.php, http://www.pornomedia.com/extra/strange/wwbeauty.
Online Greeting Cards
Online greeting card sites. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://123greetings.com, http://greeting-cards.com.
Open HTTP Proxies Internet-hosted proxies that are available to anyone. Parked Domains
URLs that host limited content or click-through ads that may generate revenue for the hosting entities but generally do not contain content useful to the end user. Under construction sites, folders, and web server default home pages. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://000.com, http://buythisdomain.com.
Pay to Surf
Sites that pay users in the form of cash or prizes, for clicking on or reading specific links, email, or web pages. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://cashcrate.com, http://inboxdollars.com.
Peer to Peer
Peer-to-peer clients and access. Torrents, music download programs. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://mininova.org, http://bitcomet.com/.
Personal Sites and Blogs
Personal websites and blogs posted by individuals or groups. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://blogger.com, http://wordpress.org.
Personal Storage
Online storage and posting of files, music, pictures, and other data. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://box.net, http://freefilehosting.net.
Philosophy and Political Advocacy
Politics, philosophy, discussions, promotion of a particular viewpoint or stance to further a cause. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://deomcrats.org, http://political.com.
Phishing and Other Frauds
Phishing, pharming, and other sites that pose as a reputable site, usually to harvest personal information from a user. These sites are typically quite short-lived, so examples do not last long. For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phishing".
Private IP Addresses Private IP addresses that are used as the host part of a URL. Proxy Avoidance and Anonymizers
Proxy servers and other methods to gain access to URLs in any way that bypasses URL filtering or monitoring. Web-based translation sites that circumvent filtering. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://anonymouse.org, http://surfen-op-school.com.
Questionable
Tasteless humor, get-rich-quick sites, and sites that manipulate the browser user experience or client in some unusual, unexpected, or suspicious manner. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://9gag.com, http://collegehumor.com.
Real Estate
Information about renting, buying, or selling real estate or properties. Tips about buying or selling a home. Real estate agents, rental or relocation services, and property improvement. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://prudentialproperties.com, http://realtor.com.
Recreation and Hobbies
Information, associations, forums and publications about recreational pastimes such as collecting, kit airplanes, outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, rock climbing, specific arts, craft, or techniques. Animal- and pet-related information, including breed specifics, training, shows, and humane societies. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://petloverspublications.com, http://craftster.org.
Reference and Research
Personal, professional, or educational reference material, including online dictionaries, maps, census, almanacs, library catalogs, genealogy, and scientific information. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://reference.com, http://wikipedia.org.
Religion
Conventional or unconventional religious or quasi-religious subjects. Churches, synagogues, or other houses of worship. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://therocksandiego.org, http://biblesociety.ca.
Search Engines
Search interfaces using key words or phrases. Returned results may include text, websites, images, videos, and files. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://google.com, http://sogou.com.
Self-Harm URLs promoting anorexia, bulimia, and other types of self-harm. Examples of websites that fall into this category: https://lostallhope.com and https://poemsofselfharm.tumblr.com. Sex Education
Information about reproduction, sexual development, safe sex practices, sexually transmitted diseases, sexuality, birth control, sexual development, tips for better sex. Products used for sexual enhancement, and contraceptives. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://sexetc.org, http://healthywomen.org/healthcenter/sexual-health.
Shareware and Freeware
Software, screensavers, icons, wallpapers, utilities, ringtones. Downloads that request a donation, open source projects. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://download.com, http://sourceforge.net.
Shopping
Department stores, retail stores, company catalogs, and other sites that allow online consumer or business shopping and the purchase of goods and services. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://amazon.com, http://groupon.com.
Social Network
Social networking sites that have user communities in which users interact, post messages, pictures, and otherwise communicate. These sites were formerly part of Personal Sites and Blogs, but have been moved to this new category to allow for differentiation and more granular policy. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://facebook.com, http://twitter.com.
Society
A variety of topics, groups, and associations relevant to the general populace, broad issues that impact a variety of people, including safety, children, societies, and philanthropic groups. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://dar.org, http://unicefusa.org.
Spam URLs
URLs contained in spam. For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spam_(electronic).
Sports
Team or conference web sites, international, national, college, professional scores and schedules; sports-related online magazines or newsletters, fantasy sports, and virtual sports leagues. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://nba.com, http://schoenen-dunk.de.
Spyware and Adware
Spyware or adware sites that provide or promote information gathering or tracking that is unknown to, or without the explicit consent of, the end user or the organization. Unsolicited advertising popups and programs that may be installed on a user's computer. For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spyware.
Streaming Media
Sales, delivery, or streaming of audio or video content, including sites that provide downloads for viewers. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://youtube.com, http://ustream.tv, http://warpradio.com.
Swimsuits & Intimate Apparel
Swimsuits, intimate apparel, or other types of suggestive clothing. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://victoriassecret.com, http://www.jockey.com.
Training and Tools
Distance education and trade schools, online courses, vocational training, software training, skills training. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://trainingtools.com, http://prezi.com.
Translation
URL and language translation sites that allow users to see URL pages in other languages. These sites can also allow users to circumvent filtering as the target page's content is presented within the context of the translator's URL. These sites were formerly part of Proxy Avoidance and Anonymizers, but have been moved to this category to allow for differentiation and more granular policy. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://translate.google.com, http://microsofttranslator.com.
Travel
Airlines and flight booking agencies. Travel planning, reservations, vehicle rentals, descriptions of travel destinations, or promotions for hotels or casinos. Car rentals. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://cheapflights.com, http://expedia.com.
Uncategorized Sites that are not in the categorization database. Unconfirmed spam sources URLs that are suspected of being involved in the distribution of spam. Unverified Versa uses advanced AI/ML (Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning) techniques to identify Typosquatting, Punycode in URLs, and character substitution in URLs. If the categories of such URLs are already known, then further action is taken based on Real Time Protection Policy rules or a URL Filtering Profile. If the category is unknown, and the URL closely matches other known FQDNs, then this "Unverified" category is returned. A tenant administrator could block such URLs or specify some other action, such as redirect to Captive Portal. Violence
Sites that advocate violence, depictions, and methods, including game/comic violence and suicide. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://happytreefriends.com, http://torturegame.org.
Weapons
Sales, reviews, or descriptions of weapons such as guns, knives or martial arts devices, or provide information about their use, accessories, or other modifications. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://browning.com, http://e-gunparts.com.
Web Advertisements
Advertisements, media, content, and banners. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://casalemedia.com, http://justwebads.com.
Web-Based Email
Sites offering web-based email and email clients. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://google.com/mail, http://foxmail.com.
Web Hosting Sites
Free or paid hosting services for web pages and information concerning their development, publication, and promotion. Examples of websites that fall into this category: http://siteground.com, http://bluehost.com.
- Click Next to configure match criteria based on users and groups.
Configure SASE Users and Groups, User Confidence Bands, and User Device Groups for Internet Protection Rules
You create user and group security rules to detect the users and groups who are using applications on your network. These rules can help to identify users who may have transferred files or transmitted threats. User and group rules identify users based on their name or role rather than their IP address. In Releases 12.2.2 and later, you can also select the user confidence bands and user device groups to include in the match criteria.
To configure users and groups, user confidence bands, and user devices groups match criteria:
- In the Create Internet Protection Rule screen, select Step 2, User & Groups. By default, all users and groups, user confidence bands, and user device groups are included in the match.

- To accept the default, click Next to continue to Step 3, Endpoint Posture.
- To change the users and groups to include in the match list, click Customize in the Users & Groups box. The Users & Groups screen displays with All Users selected by default.

- You can choose the following user types to include in the match list:
- All Users—Apply the security policy to all users, whether whether they are authenticated (known) or not authenticated (unknown)
- Selected Users—Apply the security policy to users or groups from IdP that you select
- Known Users—Apply the security policy to all authenticated users
- Unknown Users—Apply the security policy only to users that are not authenticated
- If you choose Selected Users, the following screen displays. You can choose user groups, individual users, or both user groups and users to include.

- In the Enable Internet Protection for the Following Matched Users or User Groups field, select one or more users or user groups.
- In the Search for User Groups bar, select the group to use.
- Under the User Groups tab, select the user groups to include in the match list, or type the name of a user group in the search box and then select it from the search results.
- To create a new user group based, click + Add New User Group. In the Add User Group window, enter a user group name and a distinguished name (DN) in the fields provided.

- Click Add.
- To enable internet protection for selected users, click the Users tab in the submenu. The following screen displays.

- In the Enable Internet Protection for the Following Matched Users or User Groups field, select one or more users or user groups.
- Under the Users tab, select the users to include in the match list, or type the name of a user in the search box and then select it from the search results.
- To create a new user, click + Add New User. In the Add User window, enter a username and the user's work email in the fields provided.

- Click Add.
- Click Back to return to the main Users & Groups screen.
- To change the user confidence bands to include in the match list, click Customize in the User Confidence Bands box. The following screen displays.

- Select one or more confidence bands from the drop-down list. The options are:
- Trustworthy
- Low Risk
- Moderate Risk
- High Risk
- Suspicious
- Click
 Back to return to the main Users & Groups screen.
Back to return to the main Users & Groups screen. - To change the user device groups to include in the match list, click Customize in the User Device Groups box. The following screen displays.
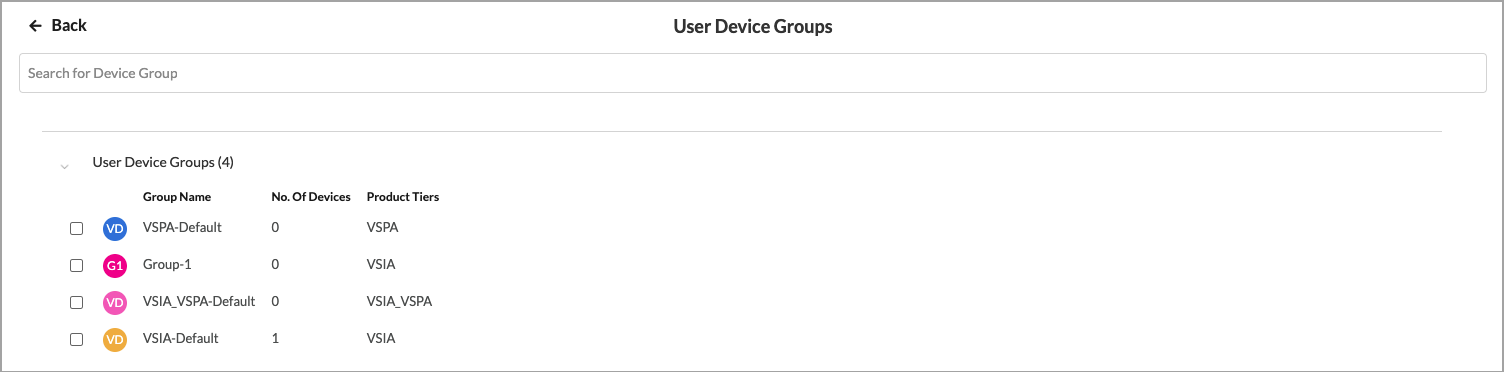
- Select one or more user device groups to include in the match list.
- Click Back to return to the main Users & Groups screen, or click Next to continue to Step 3, Endpoint Posture match criteria.
Configure Endpoint Posture for Internet Protection Rules
For Release 12.2.1 and later.
Endpoint posture allows you to select predefined and user-defined Endpoint Information Profiles (EIP) to include in the match criteria for internet protection rules. For information about configuring EIPs, see Configure Endpoint Information Profiles.
Endpoint posture also allows you to create additional match criteria by choosing a device/endpoint risk score to attribute to the entities within the network’s policy rule. This score helps determine the credibility and the likelihood of activities being legitimate or malicious. These match criteria can then be used when creating policies and rules. For more information, see Configure Endpoint Detection and Response.
To select EIPs to include in internet protection rule match criteria:
- In the Create Internet Protection Rule screen, select Step 3, Endpoint Posture. The following screen displays.

- To customize an EIP, click Customize in the EIP pane. The following screen displays.

- To create a new EIP profile, click
 Create New EIP Profile. For more information, see Configure Endpoint Information Profiles.
Create New EIP Profile. For more information, see Configure Endpoint Information Profiles. - To add a user-defined EIP, select the User Defined tab, then click
 Add Existing EIP Profile. In the Add User Defined EIP Profiles popup window, select an EIP profile from the drop-down list.
Add Existing EIP Profile. In the Add User Defined EIP Profiles popup window, select an EIP profile from the drop-down list.

- Click Add.
- To add additional user-defined EIP profiles, repeat Steps 2 and 3.
- To add a predefined EIP profile, select the Predefined tab in the Endpoint Information Profile (EIP) screen, then click
 Add Existing EIP Profile. In the Add Predefined EIP Profiles popup window, select an EIP profile from the drop-down list.
Add Existing EIP Profile. In the Add Predefined EIP Profiles popup window, select an EIP profile from the drop-down list.

- Click Add.
- To add additional predefined EIP profiles, repeat Steps 5 and 6.
- Click the
 Back arrow to return to the Endpoint Posture screen.
Back arrow to return to the Endpoint Posture screen.
To configure a device/endpoint risk score:
- In the Endpoint Posture screen, click Customize in the Device/Endpoint Risk Score pane. The following screen displays.

- Select one or more entity risk scores from the list. The options are:
- High Risk (80–100)
- Suspicious (60–80)
- Moderate Risk (40–60)
- Low Risk (20–40)
- Trustworthy (0–20)
- Click the
 Back arrow to return to the Endpoint Posture screen, or click Next to go to Step 4, Geo Locations.
Back arrow to return to the Endpoint Posture screen, or click Next to go to Step 4, Geo Locations.
Configure SASE Geographic Location for Internet Protection Rules
Versa SASE internet protection rules provide a list of predefined regions that you can use to create filter profiles based on geographic location for both source and destination. By default, all source and destination locations are included in the match list. This means that no filtering is done based on location and traffic flows to all destinations. You can customize the location by selecting the country, state, and city to include in the match list.
To configure geographic location internet protection rule match criteria:
- In the Create Internet Protection Rule screen, select Step 4, Geo Locations.

- To accept the default, click Next to continue to Step 5, Network Layer 3-4 match criteria.
- To change the source geographic locations to include in the match list, click Customize under Source Geolocation. The Source Geo Location screen displays.

- Click Clear All to remove all the default source locations. (Because all locations are selected by default, they are not displayed).
- (For Releases 12.2.1 and later.) To customize the geographic location by by country, state, or city, click the down arrow in the Country box. The Selected section lists the country, state, or city with name and location type.
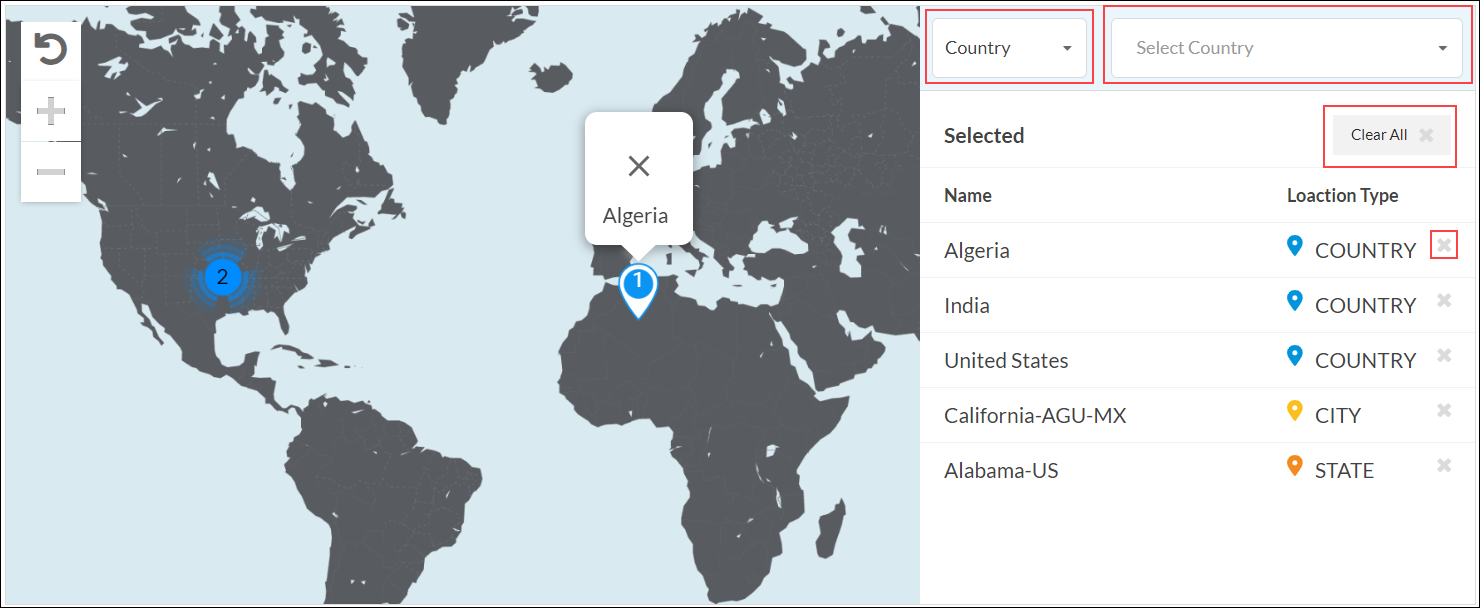
- Select Country, and then select one or more countries from the list. The map changes to highlight the countries that are selected.
- Select State, and then enter the name of the state and select the state from the list.
- Select City, and then enter the name of the city and select the city from the list.
- To remove a location from the selected list, click the X next to the location type name.
- To remove all locations from the selected list, click Clear All.
- In the Source Geo Location screen, click the
 Back arrow to go to Step 4, Geo Locations screen.
Back arrow to go to Step 4, Geo Locations screen. - To customize the destination geographic locations to include in the match list, click Customize under Destination Geo Location. The Destination Geo Location screen displays.

- Click Clear All to remove all the default destination locations. (Because all locations are selected by default, they are not displayed).
- Repeat Steps 5 to 7 to change the destination locations.
- Click Next to go to Step 5, Network Layer 3-4 screen, or click the
 Back arrow to return to the Step 4, Geo Location screen.
Back arrow to return to the Step 4, Geo Location screen.
Configure SASE Network Layer 3 and Layer 4 Criteria for Internet Protection Rules
You can create internet protection rule match criteria based on the following:
- Services—You can create match criteria based on Layer 4 services. Versa supports 741 predefined Layer 4 services. You can also create your own services.
- Source and destination of traffic—You can create match criteria based on Layer 3 source and destination addresses, source sites and zones, and destination sites and zones.
- Schedules—You can create schedules that set a start time and date and an end time and date during which the policy will be in effect.
To configure network rules based on network Layer 3 and Layer 4 match criteria:
- In the Create Internet Protection Rule screen, select Step 5, Network Layer 3-4. By default, all Layer 4 services and all source and destination traffic is included in the match, and no schedules have been configured.

- To accept these defaults, click Next to continue to Step 6, Security Enforcement rules.
Customize Services Match Criteria
You can configure internet protection rules to filter traffic according to the network service being provided. By default, all network services are selected, which means that security enforcement rules are applied to the traffic of all network service types. If desired, you can specify the services to which to apply security enforcement rules.
To customize match criteria based on Layer 4 services:
- Click Customize in the Services box. The Services popup window displays. By default, all services are listed.
- In the All Services box, click the down arrow to select either Predefined or User-Defined services. The list of services is updated to display the selected services.
- To add a new user-defined service, click
 Add User Defined. The following screen displays.
Add User Defined. The following screen displays.

- Select a protocol or a port number. The available options are AH, ESP, TCP, UDP, ICMP, or 0 through 255. If you select TCP, UDP, or TCP and UDP, the following popup window displays.

- Under Port, select either Source AND Destination or Source OR Destination, as follows:
- Source AND Destination—Select both a source port number and a destination port number (range 0 through 255)
- Source OR Destination—Select either a source port number or a destination port number (range 0 through 255)
- Click Next to to the Name and Tags step, then enter the following information.

Field Description Name Enter a name for the rule. Description (Optional) Enter a description of the rule. Tags (Optional) Add one or more tags. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no spaces or special characters. You can specify multiple tags added for the same object. The tags are used for searching the objects. Edit Click the  Edit icon to make any needed changes to your selections.
Edit icon to make any needed changes to your selections. - Click Save to save the new service. You can then select the service in the drop-down list. For information about creating user-defined services, see Configure SASE User-Defined Objects.
- In the Services screen, select the Layer 4 services to include in the rule, then click the
 Back arrow icon to return to the Network Layer 3-4 screen. From this screen you can customize source and destination information and configure policy schedules.
Back arrow icon to return to the Network Layer 3-4 screen. From this screen you can customize source and destination information and configure policy schedules.
Customize Source and Destination Match Criteria
To customize match criteria based on Layer 3 source and destination information:
- Click Customize in the Source & Destination (Layer 3) box. In the Source & Destination (Layer 3) screen, select Source Address tab, and then enter information for the following fields. Note that in Releases 11.3.2 and earlier, you configure the source and destination on a single screen.

Field Description Negate Source Address Select to apply the rule to any source addresses except the ones in the Source Address field. IP Subnet Enter a list of comma-separated subnets to include in the match list, for example, 10.2.1.0/24. IP Range Enter a list of comma-separated IP addresses or ranges to include in the match list, for example,10.2.1.1–10.2.2.2. IP Wildcard Enter a list of comma-separated IP addresses and masks to include in the match list, for example, 192.68.0.56/255.255.0.255. VPN Name (For Releases 12.2.1 and later.) Select the VPN through which the IP address is reachable. - To create an address group, click
 Add Address Group in the Source Address tab. In the Enter Addresses section of the Address Group popup window, enter information for the following fields. You configure the address groups in the User-Defined Objects section. If you want to configure one or more specific source IP addresses, you do not need to select an address group. Instead, use the IP Wildcard field to enter the IP addresses.
Add Address Group in the Source Address tab. In the Enter Addresses section of the Address Group popup window, enter information for the following fields. You configure the address groups in the User-Defined Objects section. If you want to configure one or more specific source IP addresses, you do not need to select an address group. Instead, use the IP Wildcard field to enter the IP addresses.

Field Description Type Select the type of IP address to match and the value to match. The name of the Address/Prefix field changes depending on the value you select in the Type field.
- Subnet
- IP Range
- IP Wildcard
- IPv6 Subnet
- FQDN
- Dynamic Address
- Subnet
Enter one or more IP addresses and subnet masks, for example, 10.2.1.0/24. - IP Range
Enter one or more IP addresses within the IPv4 address range specified in the IPv4 Range field, for example, 10.2.1.1–10.2.2.2.
- IP Wildcard
Enter one or more wildcard masks for specific IP addresses, for example, 192.68.0.56/255.255.0.255. - IPv6 Subnet
Enter one or more IP addresses and subnet masks within the IPv6 subnet range specified in the IPv6 subnet.
- FQDN
Enter one or more IP addresses returned in a DNS query that resolves the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) into an IP address. The FQDN cannot contain any wildcard characters. - Dynamic Address
Enter a dynamic address object, which is a container for an IP address list that can change dynamically. - Address Files
(For Releases 12.2.1 and later.) When you select the Address Files type, select an address file. For more information, see Manage Files and Folders.
To add a new address file:
- Click Add new file.

- In the Upload File popup window, click Browse and select an address file to upload. The file must be in CSV format.

- Click Upload.
- To add IP address types, click the
 Add icon. To remove an address type, click the
Add icon. To remove an address type, click the  Minus icon.
Minus icon. - Click Next. In the Name and Tags section, enter a name (required) and, optionally, tags.
- Click Save.
- Select the Destination Address tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Negate Destination Address Select to apply the rule to any destination addresses except the ones in the Destination Address field. IP Subnet Enter a list of comma-separated subnets to include in the match list, for example, 10.2.1.0/24. IP Range Enter a list of comma-separated IP addresses or ranges to include in the match list, for example,10.2.1.1–10.2.2.2. IP Wildcard Enter a list of comma-separated IP addresses and masks to include in the match list, for example, 192.68.0.56/255.255.0.255. - To create an address group, perform Steps 2 through 5.
- Select the Source Zones and Sites tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

In the Source Zones field, select one or more source zones to include in the match list. By default, three source zones are available. User-defined zones, such as zones for IPsec and GRE tunnels, also display in this list, and you can select them.- Internet—Select this zone if traffic comes from the internet.
- SD-WAN Zone—Select this zone if traffic comes from an SD-WAN device.
- VSA Application—Select this zone if traffic comes from a VSA client application.
- In the Source Sites field, select one or more source sites to include in the match list.
- Select Destination Zones and Sites tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

- In the Destination Zones field, select one or more destination zones to include in the match list. User-defined zones, such as zones for IPsec and GRE tunnels, also display in this list, and you can select them. By default, two destination zones are available:
- SD-WAN Zone—Select this zone if traffic comes from an SD-WAN device.
- Versa Client—Select this zone if traffic comes from a VSA client application
- In the Destination Sites field select one or more destination sites to include in the match list.
- In the Destination Zones field, select one or more destination zones to include in the match list. User-defined zones, such as zones for IPsec and GRE tunnels, also display in this list, and you can select them. By default, two destination zones are available:
- Click the
 Back arrow icon to return to the Network Layer 3-4 screen.
Back arrow icon to return to the Network Layer 3-4 screen.
Configure Schedules
To configure schedules that set a start time and date and an end time and date during which the policy will be in effect:
- Click Customize in the Schedule box.

The Schedule screen displays.

- If you have already configured one or more schedules, click the down arrow to select a schedule, the click the
 Back arrow icon to return to the Network Layer 3-4 screen or click Next to go to Step 6, Security Enforcement.
Back arrow icon to return to the Network Layer 3-4 screen or click Next to go to Step 6, Security Enforcement. - To add a new schedule, click
 Add New. The following screen displays.
Add New. The following screen displays.

- In the Enter Schedule Details section, enter information for the following fields.
Field Description Recurrence Select None, Daily, or Weekly. - None
If you select None, enter the following information to set a start and end time for the policy to be in effect:
- Start Date—Select a start date.
- Start Time—Select a start time.
- End Date—Select an end date.
- End Time—Select an end time.
- Daily
If you select Daily, enter information for the following fields:

- All Day—Click the slider to schedule the security policy to be in effect all day.

- Start Time—Select a start time from the drop-down list.
- End Time—Select an end time from the drop-down list.
- Weekly
If you select Weekly, enter information for the following fields:

- All Day—Click the slider to schedule the security policy to be in effect all day.

- Start Time—Select a start time.
- End Time—Select an end time.
- Select the days the security policy is to be in effect.

-
Click Next. The Name and Tags section displays.
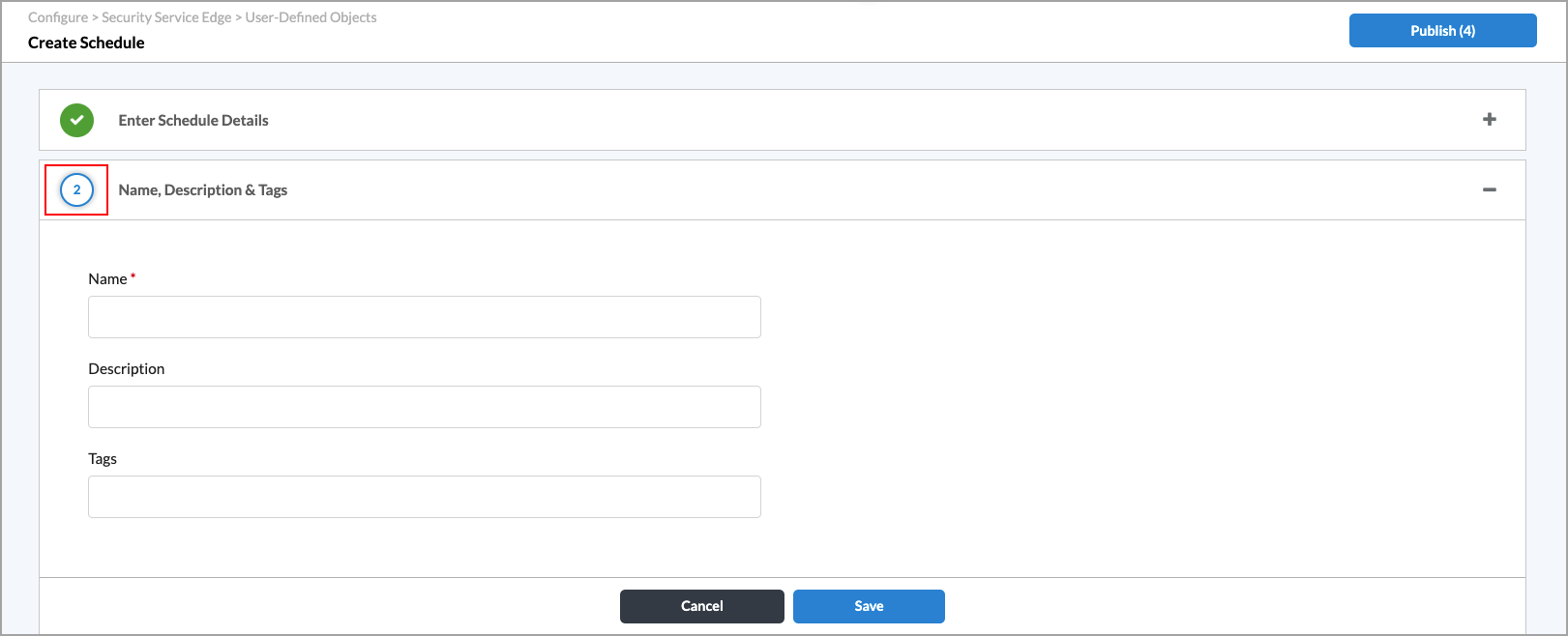
-
Enter a name for the new schedule and, optionally, one or more tags to include. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no spaces or special characters that you use for searching objects.
- Click Save. You can now use the new schedule when creating rules.
Configure Security Enforcement Actions for SASE Internet Protection Rules
You use Versa SASE security enforcement rules to define the actions to take on traffic that meets previously defined match conditions and to define the security enforcement actions that you can apply to matching traffic. You can select profiles under Filtering Profiles, Malware Protection & IPS, Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Data Loss Prevention (DLP) profiles, Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), and Remote Browser Isolation (RBI), as shown below.
Note: In Release 12.2.2, under the Security Enforcement tab, the Secure Web Gateway (SWG) subtab was renamed Filtering Profiles and a new Malware Protection & IPS subtab was created, which contains the Malware Protection and Intrusion Protection System (IPS) profiles.

You can apply either one security enforcement action or one security enforcement profile to matching traffic.
You can specify the following security enforcement actions:
- Allow—Allow all traffic that matches the rule to pass unfiltered.
- Deny—Drop all traffic that matches the rule.
- Reject—Drop the session and send a TCP reset (RST) message or a UDP ICMP port unreachable message.
- Profiles—Allow all traffic that match the selected security profile rules.
For Filtering Profiles, you can choose a predefined security enforcement profiles to allow or reject traffic, or you can create a customized version of any of the predefined profiles. The following are the predefined Filtering Profiles security enforcement profiles:
- URL filtering—Prevents access to specific URLs, controlling access to secure (HTTPS) and unsecure (HTTP) websites, thus allowing you to limit web-browsing activity and reduce risks from uncontrolled access to internet websites, including threat propagation, loss of data, and lack of compliance.
Note: In addition to using predefined URL-filtering profiles, you can create custom URL-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom URL-Filtering Profiles.
- IP filtering—Identifies network traffic based on the source or destination IP address or fully qualified domain name (such as www.acme.com) and filters or blocks traffic based on its IP address or FQDN and based on the reputation associated with an IP address or FQDN and its geographic location.
Note: In addition to using predefined IP-filtering profiles, you can create custom IP-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom IP-Filtering Profiles. - File filtering—Reduces the risk of attacks from unwanted and malicious files, protecting against virus and vulnerabilities that are associated with various types of files. File filtering is performed based on the file type and the hash of the file. File filtering can block files associated with specific applications, files of specific sizes, files associated with specific protocols, and files traveling in a particular direction.SHA-based hash lists of files can mark potentially dangerous files for blocking and to mark safe files for allowing. File filtering to perform reputation-based file hash lookups on a cloud server.
Note: In addition to using predefined file-filtering profiles, you can create custom file-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom File-Filtering Profiles. - Domain Name System (DNS) filtering—Blocks access to websites, webpages, and IP addresses, to provide protection from malicious websites, such as known malware and phishing sites.
Note: In addition to using predefined DNS-filtering profiles, you can create custom DNS-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom DNS-Filtering Profiles.
For Malware Protection & IPS, you can choose the following profiles:
- Malware protection—Scans web and email traffic for all types of malicious software (malware), which is a file or code that infects, explores, steals or otherwise damages servers and host devices.
- Intrusion protection system (IPS)—Identifies malicious activity using signatures, which are rules for matching suspicious software or patterns in an application's traffic, and by monitoring for unusual events or trends in network traffic.
For Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), you can use custom CASB profiles or add CASB profiles from the CASB tab. For more information, see Configure CASB Profiles.
For Data Loss Prevention (DLP), you can use predefined or user-defined profiles. For more information, see Configure Data Loss Prevention in Concerto.
For Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), you can use predefined or user-defined profiles. For more information, see Configure Advanced Threat Protection.
For Remote Browser Isolation, you can use user-defined profiles. For more information, see Configure Remote Browser Isolation.
By default, the Filtering Profiles and Malware & IPS profiles have predefined VersaEasy configurations. You can use the predefined VersaEasy configurations, or you can create a custom profile.
Note: The security profiles that are available to a tenant depend on which product you choose for the tenant when the tenant is created.
Configure a URL-Filtering Profile for SASE Internet Protection Rules
By default, Versa SASE provides a predefined security enforcement policy for URL filtering. You can customize the predefined URL-filtering protection profile.
In addition to using predefined URL-filtering profiles, you can create custom URL-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom URL-Filtering Profiles.
To apply a URL-filtering protection profile:
- In the Filtering Profiles tab, select URL Filtering to enable the preselected EasyURLFiltering security enforcement policies. By default, the EasyURLFiltering policies provide URL filtering for the following types of websites:
- Adult and pornography
- Games
- Web advertisements

- To change the default settings, click the down arrow.
Note: The URL-filtering profile below includes user-defined profiles in addition to predefined profiles. For more information, see Configure Custom URL-Filtering Profiles.

- Select one of the URL filters to enable only that filter. Select EasyURLFiltering to restore the default URL filtering.
- Select other security profiles to customize, or click Next to continue.
Configure an IP-Filtering Profile for Internet Protection Rules
Traffic passing through the network may have IP addresses that may cause security risks to your network. By default, Versa SASE provides a predefined security enforcement policy to filter traffic by IP address. You can customize the IP-filtering profile if desired.
In addition to using predefined IP-filtering profiles, you can create custom IP-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom IP-Filtering Profiles.
To apply an IP-filtering profile:
- In the Filtering Profiles tab, select IP Filtering to enable the preselected IP-filtering security enforcement policies. By default, traffic associated with the following types of security risks generates alerts:
- Denial of service
- Network
- Phishing
- Reputation
- Scanners
- Spam sources
- Web attacks
By default, traffic associated with the following types of security risks is rejected:
- Botnets
- Proxy
- Window exploits

- To change the default settings, click the down arrow.
Note: The IP-filtering profile below includes user-defined profiles in addition to predefined profiles. For more information, see Configure Custom IP-Filtering Profiles.
- Select one of the items listed under User Defined or VersaEasy™ to enable only that filter. Note that you can choose only one of the filtering items. Select Versa Recommended Profile to restore the default IP-filtering settings.
- Select other security profiles to customize, or click Next to continue.
Configure a File-Filtering Profile for Internet Protection Rules
File filtering helps to reduce the risk of attacks from unwanted and malicious files associated with various protocols. By blocking the transfer of potentially dangerous files and types of files, you decrease an attacker's ability to attack your organization.
In addition to using predefined file-filtering profiles, you can create custom file-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom File-Filtering Profiles.
To apply a file-filtering profile:
- In the Filtering Profiles tab, select File Filtering to enable the preselected file-filtering security enforcement policies. By default, files associated with the following protocols generate alerts. You cannot change the default file-filtering alert settings.
- EXE
- HTML
- PDF

- To change the default settings, click the down arrow.
Note: The file-filtering profile below includes user-defined profiles in addition to predefined profiles. For more information, see Configure Custom File-Filtering Profiles.

- Select one of the items listed to enable only that filter. Select EasyFileFiltering to restore the default file-filtering settings.
- Select other profiles to customize, or click Next to continue.
Configure a DNS-Filtering Profile for Internet Protection Rules
Domain Name System (DNS) filtering blocks access to DNS queries for websites, webpages, and IP addresses, to provide protection from malicious websites, such as known malware and phishing sites. DNS filtering uses the DNS service to block web sites either by domain name or by IP address.
In addition to using predefined DNS-filtering profiles, you can create custom DNS-filtering profiles and associate them with internet protection rules. For more information, see Configure Custom DNS-Filtering Profiles.
To configure a DNS-filtering profile:
- In the Security Enforcement screen > Secure Web Gateway (SWG) tab, select DNS Filtering in the Profiles section to enable the preselected DNS-filtering security enforcement policies. By default, the following cloud service file types generate alerts:
- Bad traffic
- Bots
- DoS
- Spam
- Scanners
- Unwanted applications
- Window exploits

- To change the default settings, click the down arrow.
Note: The DNS-filtering profile below includes user-defined profiles in addition to predefined profiles. For more information, see Configure Custom DNS-Filtering Profiles.
- Select one of the items listed to enable only that filter. Select EasyDNS to restore the default file-filtering settings.
- Select other profiles to customize, or click Next to continue.
Configure a Malware Protection Profile for SASE Internet Protection Rules
Malware is malicious software software that is specifically designed to disrupt computers and computer systems. There are many types of malware, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan viruses, spyware, adware, and ransomware. Among the things malware can do is leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, and deprive users access to information.
By default, Versa SASE provides a predefined security enforcement policy to protect against malware. You can customize the malware protection profile.
To configure a malware protection profile:
- Go to Configure > Real-Time Protection > Internet Protection. The Internet Protection Rules List screen displays all configured internet protection rules.
- Click the
 Add icon to create a rule. The Create Internet Protection Rule screen displays.
Add icon to create a rule. The Create Internet Protection Rule screen displays. - Select the Security Enforcement action.

- Select the Malware Protection & IPS tab, and then click in the Malware Protection box to enable the default EasyMalwareProtection security enforcement profile. By default, the EasyMalwareProtection profile blocks the following types of malware:
- Adware
- Ransomware
- Spyware
- Trojans
- Unwanted applications
- Viruses
- Worms
- Click the down arrow to display other options.

- Select a user-defined or VersaEasy™ malware protection profile. If you select VersaEasy, choose one of the following:
- Scan Email Traffic to send alerts about the following malware in both the upload and download directions:
- IMAP
- MAPI
- POP3
- SMTP
- Scan Web Traffic to deny the following malware in both the upload and download directions:
- FTP
- HTTP
- Select EasyMalwareProtection to restore the default EasyMalware protection settings.
- Scan Email Traffic to send alerts about the following malware in both the upload and download directions:
- Select other security profiles to customize or click Next to continue.
Configure an IPS Profile for SASE Internet Protection Rules
The intrusion prevention system (IPS) mitigates security vulnerabilities by responding to inappropriate or anomalous activity. Responses can include dropping data packets and disconnecting connections that are transmitting unauthorized data.
By default, Versa SASE provides a predefined IPS enforcement policy. You can customize the IPS profile.
Note: The IPS profile displays only if the tenant is subscribed to the SWG and VSA Professional services.
To configure an IPS profile:
- In the Malware Protection & IPS tab, select Intrusion Protection System (IPS) to enable the preselected EasyIPS filtering security enforcement policies. By default, the following vulnerabilities are blocked from all servers and clients:
- High-severity and medium+ confidence attacks
- Medium+ common vulnerability scoring system (CVSS) and medium+ confidence attacks

- To override a predefined IPS profile, you can click the down arrow in the Predefined IPS Profile Override field and select a user-defined IPS profile. To configure a user-defined IPS override profile, see Configure IPS Override.
- To change the default settings, click the down arrow.

- Select one of the user-defined or VersaEasy IPS filters listed to enable only that filter. Select EasyIPS to restore the default IPS-filtering settings.
- Select other security profiles to customize, or click Next to continue.
Configure a CASB Profile for Internet Protection Rules
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) is on-premises or cloud-based policy enforcement software that secures the data flowing between users and cloud applications to comply with corporate and regulatory requirements. CASB applies enterprise security policies when users access cloud-based resources.
You can associate a CASB profile with a SASE internet protection rule to allow or deny traffic. CASB secures the data flowing between users and cloud applications to comply with corporate and regulatory requirements. For more information, see Configure CASB Profiles.
To associate a CASB profile with a SASE internet protection rule:
- In the Security Enforcement screen, select Profiles. Then, select the Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB - Inline) tab and click the slider bar to enable CASB.

- Select an item from the drop-down list, and then select the CASB profile to associate with the internet protection rule.

- To add a CASB profile, click Create New. The Create Cloud Access Security Broker Profile screen displays. For more information, see Configure CASB Profiles.
- Click Next to continue.
Configure a DLP Profile for Internet Protection Rules
To oversee, track, and report all data transactions in the network and to scan all content that passes through an organization's ports and protocols to ensure data security in the organization you associate a DLP profile with a SASE internet protection rule. DLP provides a set of tools and processes for detecting and preventing data breaches, cyber exfiltration, and unwanted destruction of sensitive data. You use DLP to protect and secure an organization's data and to comply with regulations. To create DLP profiles, see Configure Data Loss Prevention in Concerto.
To associate a DLP profile with a SASE internet protection rule:
- In the Security Enforcement screen, select Profiles, and then select the Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tab.

- Click the slider to enable DLP, and then choose a DLP profile.

- Click Next to continue.
Configure an ATP Profile for Internet Protection Rules
Versa advanced threat protection (ATP) provides mechanisms that detect zero-day threats and prevent these threats from affecting organizations. To enforce Versa ATP detection mechanisms for internet traffic, you associate an ATP profile with a SASE internet protection rule. For more information, see Configure Advanced Threat Protection.
To associate an ATP profile with a SASE internet protection rule:
- In the Security Enforcement screen, select Profiles. Then select the Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) tab and click the toggle to enable ATP.

- Select the ATP profile to associate with the internet protection rule.
- To create a new ATP profile, click + Create New. The Create ATP Profile screen displays. For more information, see Configure ATP Profiles.
- Click Next to review and then click Save.
- Click Next to continue.
Configure an RBI Profile for Internet Protection Rules
To associate a remote browser isolation profile with a internet protection rule:
- Go to Configure > Real-Time Protection > Internet Protection.
- In the Security Enforcement screen, select Profiles. Then select the Remote Browser Isolation (RBI) tab and click the toggle to enable RBI.

- Select the RBI profile to associate with the internet protection rule.
- To create a new RBI profile, click + Create New. The Create Remote Browser Isolation Profile screen displays. For more information, see Configure Remote Browser Isolation.
- Click Next to review and then click Save.
- Click Next to continue.
Review and Deploy Internet Protection Rules
The final step in configuring internet protection rules is to review the choices you have made, edit them if needed, and then deploy the rule.
To review and deploy the internet protection rule:
- In the Security Enforcement screen, select Review and Deploy and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the rule. The name can be a maximum of 63 characters and can include alphanumeric characters, underscores, and hyphens. Description (Optional) Enter a description for the rule. Tags (Optional) Enter a text string or phrase to associate with the rule. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no white spaces or special characters that you can use to search rules. You can specify multiple tags. Rule is Enabled Click the slide bar to enable the rule:

Click the slide bar again to disable the rule:

- To modify the information in a section, click the
 Edit icon, then make the changes to the configuration.
Edit icon, then make the changes to the configuration. - Click Save to deploy the new internet protection rule.
Supported Software Information
Releases 11.1.1 and later support all content described in this article, except:
- Release 11.4.1 provides separate tabs for Source Address, Destination Address, Source Zones and Sites, and Destination Zones and Sites for SASE Source and Destination Traffic for Internet Protection Rules.
- Release 12.1.1 allows you to clone Internet Protection Rules.
- Release 12.2.1 adds support to customize geographic locations by country, region, and city, and supports the VPN name option to include in the source address match list; allows you to create additional match criteria by choosing a device/endpoint risk score to attribute to the entities within the network’s policy rule; adds support for configuring RBI profiles; deprecated predefined applications are not displayed in the Concerto UI screens; adds support for the built-in GenAI_Firewall internet protection rule.
- In Release 12.2.2, under the Security Enforcement tab, the Secure Web Gateway (SWG) subtab was renamed Filtering Profiles and a new Malware Protection & IPS subtab was created, which contains the Malware Protection and Intrusion Protection System (IPS) profiles.
Additional Information
Configure CASB Profiles
Configure Custom DNS-Filtering Profiles
Configure Custom File-Filtering Profiles
Configure Custom IP-Filtering Profiles
Configure Data Loss Prevention in Concerto
Configure SASE Private Application Protection Rules
Configure SASE Secure Client Access Rules
