Configure WAN Connections
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
This article describes how to change the settings for WAN connections. You must configure WAN interfaces before you deploy a device. Note that the WAN configuration affects the LAN port numbering, so you must configure WAN connections first.
Note: You must configure WAN interfaces before saving the device configuration, including the following:
- Add or delete WAN interfaces.
- Choose the MPLS or internet routing technique.
- Enable the gateway feature.
- Enable the PPPoE protocol.
- Enable HA mode.
To change these settings saving, you must undeploy, change the settings, and then redeploy the configuration. See Undeploy a Device Configuration.
The following video presents an overview of WAN interfaces and configuration.
Configure a WAN
- Click Configure in the left menu bar to open the Configure dashboard.
- Hover over the device in the honeycomb and click Configure to open the site information window.

- Click Next to open the Configuration > Network screen.

- Click the WAN icon to open the Network > WAN screen.

- Click WAN1-Port0 to add one or multiple WAN interfaces.

- If needed, select the + WAN icon in the interface name drop-down menu to add a WAN. To delete the highest-numbered WAN, select it in the drop-down menu and then click the trash icon.
- Select the WAN to be configured in the drop-down menu. The WAN connection at appliance port 0 is WAN1, port 1 is WAN2, and so forth.
- Use the toggle switch to switch a WAN interface on or off.
- Click a circuit role:
- Hot Standby—For internet-bound and SD-WAN traffic, a hot-standby circuit has a lower preference than the primary circuit. You can create rules to steer traffic on the interface. Titan sends DIA traffic to a hot-standby interface only if the primary interface is down.
- Primary—The interface that sends SD-WAN and DIA traffic.
- Select the transport domain for the WAN connection. You must select the transport domain before you deploy the device:
- Internet
- MPLS
- For a hub–controller topology, toggle to switch the Hub–Controller Staging on or off, and select the staging pool size.
- In the Tunnel Selection field, choose the tunnel type:
- For an Internet transport domain:
- Internet only (Globe icon)—Select for internet access only.
- SD-WAN only (Hub icon)—Select for SD-WAN access only.
- SD-WAN and Internet (DIA) Split Tunnel (Combined Globe and Hub icon)—Select for SD-WAN and DIA.
Note: Spoke sites must have at least one WAN configured as VPN only. This configures the spoke to accept and use the default route propagated by the hub gateway for centralized internet access. It is recommended that you set only one WAN interface as VPN-only for the spoke.
- For an MPLS transport domain:
- SD-WAN only (Hub icon)—Select to have the SD-WAN interface send traffic to SD-WAN networks.
- SD-WAN and Split Tunnel (MPLS)—Select to route data packets between two networks based on network traffic from the LAN. For SD-WAN and Split-Tunnel (MPLS) traffic, you must configure EBGP in the Routing tab and you must select the Redistribution option. By default, the default VRF for the tenant is selected. See Configure Routing.
- For an Internet transport domain:
- Use the toggle switch to enable or disable remote access VPN. See Configure Remote Access VPN.
- Enter the VLAN ID for the interface.
- Enter the maximum transmission unit (MTU), in bytes. The range is 72 through 9000 bytes.
- In the Network Address field, select DHCP or Static. Note that to change the network address configuration, you must first lock the device. For more information, see Edit WAN or LTE Interfaces in an Active Device, below.
- If you select Static enter a private IP address and a gateway, and enter the primary and secondary IP addresses for DNS servers.
- For a hub–controller topology, click the NATeD toggle to enable NAT firewall and the enter the public IP address for the firewall WAN interface. Note that you cannot configure DHCP for a hub–controller.
- Click Advance Configuration (Customized) to configure advanced WAN settings, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Link Mode Select the link mode:
- Auto—This is the default.
- Full duplex
- Half duplex
Default: Auto
Link Speed Select the link speed:
- Auto—Use for link speeds about 1 Gbps. This is the default.
- 10 Mbps
- 100 Mbps
- 1 Gbps
Default: Auto
Gateway (Group of Fields) Click On or Off to enable or disable the interface as a gateway. After you enable an interface to be a gateway, the branch becomes a gateway and sends default route to its peer branch or branches. Then select the gateway topology. - Full Mesh
Select to have all peer devices receive a default route from the device that is set as the gateway. Typically, this topology is not used. - Hub (in hub-and-spoke topology)
A gateway is used in a hub-and-spoke topology to allow spokes to route traffic through the hub. To deploy and create a spoke site, you must first create a hub on which a gateway is enabled and deployed. Enabling a gateway as a hub allows you to define traffic-steering rules and policies for having the spoke perform local internet breakout for some traffic while sending all other traffic to the hub gateway. Uplink Bandwidth Enter the actual uplink bandwidth purchased from the service provider. The uplink bandwidth is to the traffic from the branch to the outside network. Downlink Bandwidth Enter the actual bandwidth downlink purchased from the service provider. The downlink bandwidth is to the traffic from the outside network to the branch. Zone Protection (Group of Fields) - Zone Protection
Select a zone protection profile. To associate a zone protection profile to a network, the profile must be pushed to the device, otherwise the configuration fails with an error.
To add a new zone protection profile, click the
 icon. For more information, see Configure Zone Protection Profiles.
icon. For more information, see Configure Zone Protection Profiles.- Logging
Click to configure logging:
- None—Click to perform no logging.
- Default—Click to use default logging.
- Custom—Click to configure logging to a customer log server. Based on the rule match, the device may send a large number of log messages.

- Please Select—If you select Custom, click the down arrow to select a log profile.
To create a new custom flow logs profile, click . For more information, see Add Custom Logs Profile.
. For more information, see Add Custom Logs Profile.
- Please Select—If you select Custom, click the down arrow to select a log profile.
Traffic Shaping (Group of Fields) Configure schedulers, which assign traffic with different drop-loss priority levels to different outbound queues. - Guaranteed Rate
Select the guaranteed transmission rate of data packets. You can define the rate as a percentage of the parent interface’s shaping rate or as the line rate.
Range: 1 through 100 percent
Default: None- Transmit Rate
Select the transmission rate for data packets. You can define this in percentage of the parent interface’s shaping rate or the line rate.
Range: 1 through 100 percent
Default: None- Drop Probability
Select the traffic class and its low/high drop probability percentage. The total guaranteed bandwidth of EF, AF, and BE traffic cannot exceed 100 percent, and the guaranteed rate percentage must be less than the transmit rate percentage. - Assured forwarding (AF)
- Best effort (BE)
- Expedited forwarding (EF)
- Network control (NC)
Ingress Traffic Shaper (Group of Fields) - Peak Rate
Enter the maximum ingress rate, in kilobits per second (Kbps).
Range: 8 through 10000000 Kbps
Default: None
- Peak Burst Size
Enter the maximum burst size, in bytes per second.
Range: 1000 through 4294967295 bytes per second
Default: None
Link Monitoring (Group of Fields) - Next-Hop
Click the toggle to enable dynamic link monitoring for next-hop reachability. - Remote IP
Enter a remote IP address for remote IP reachability through this WAN link to detect link failures. To change the network address configuration, you must first lock the device. For more information, see Edit WAN or LTE Interfaces in an Active Device, below. - Interval
Enter the frequency, in seconds, at which to send ICMP packets to the IP address.
Range: 1 through 60 seconds
Default: 3 seconds- Threshold
Enter the maximum number of ICMP packets to send to the IP address. If the IP address does not respond after this number of packets, the monitor object, and hence the IP address, is marked as down.
Range: 1 through 60
Default: 5 - Click Save to save the settings.
Configure VLAN Subinterfaces on a WAN Interface
Titan devices support VLAN-based subinterfaces. For interfaces that require VLAN support, you create multiple subinterfaces, where each subinterface maps to an individual VLAN ID. The subinterfaces map to the corresponding VLAN IDs.
To configure a VLAN subinterface on a WAN interface, you can configure the VLAN subinterface on a WAN port manually, or you can change the default WAN network template and select this template when you create a new device. You can add multiple VLAN subinterfaces to the WAN port.
Note that if you enable PPPoE on a single VLAN subinterface on a WAN port, PPPoE is automatically enabled on the other VLAN subinterfaces on the same WAN port. For example, if you enable VLAN_100 and VLAN_200 on WAN1_port0, and if you enable PPPoE on VLAN_100, PPPoE is also enabled on VLAN_200. In this scenario, if you also enable a bridge interface on PPPoE VLAN_200, you must modify the username and password on PPPoE VLAN_200 to prevent unauthorized access.
To configure VLAN subinterfaces on a Titan device, you do the following:
- Edit the default configuration template.
- Create a device with a WAN subinterface.
- Add a WAN PPPoE subinterface on an activated or deployed device.
Edit Default Configuration Template
Titan Portal provides a default configuration. You can edit the default template using the Templates menu in the left menu bar in the Titan Portal dashboard. You can select the new configuration template when you configure a new site.
If you do not want to configure a VLAN subinterface on a WAN port manually, you can change the WAN network settings in the default configuration template.
To edit the default configuration template:
- Click Templates in the left menu bar to open the templates dashboard.
- In the Device Template tab, select the default template.

- Click the WAN icon to open the Network > WAN screen.

- Click WAN1-Port0, and then click the + WAN icon to add one or multiple WAN interfaces.

- Enter the VLAN ID for the subinterface.
- Click Advance Configuration (Customized) to configure advanced WAN settings. Note that you cannot enable a bridge interface in a default template, because you cannot configure LAN settings on a bridge interface.
- Click PPPoE Status and switch the PPPoE Status toggle to on.
- To add additional VLAN subinterfaces to the WAN interface, click the
 icon, enter the VLAN ID, and then click Continue.
icon, enter the VLAN ID, and then click Continue.

- Click Save.
Create a Site with WAN Subinterface
To enable a bridge interface on a WAN subinterface, you configure a Layer 2 port and enable trunk or access interface mode on the LAN port.
To create a site with WAN subinterface:
- Click Configure in the left menu bar to open the Configure dashboard.
- Click one of the license package icons to display the available license packages.
- To add the site to the honeycomb, drag the license package onto the dashboard.

- In the New Site Configuration window, enter the required information.

- Click Save.
- Click Configure in the left menu bar to open the Configure dashboard.
- Hover over the device in the honeycomb, and click Configure to open the site information window.

- To configure a Layer 2 port for a bridge interface, click the LAN box.

- Click the Ethernet and WiFi Ports box to open the Network > LAN > Ethernet Ports screen.

- In the Ethernet Ports screen, select LAN, click the drop-down menu to view a list of available ports and corresponding LAN numbers, and then select a LAN port.

- In the Port Type field, select Switched (Layer 2).
- Select the interface mode:
- Access Mode
- Trunk Mode
- Click the Select VLAN ID drop-down menu, select the VLAN ID, and then click Continue. To add a new VLAN ID, click the
 icon.
icon. - Click Save.
- Click the WAN box to open the Network > WAN screen.

- In the Network: WAN configuration window, enter information for the following fields.

- In the WAN interface drop-down menu, select the WAN subinterface to enable bridging.
- To add a VLAN subinterface to the WAN port, click the
 icon.
icon. - Enter the VLAN ID, and then click Continue.

- Click Advance Configuration (Customized) to configure advanced WAN settings and select interface mode. Switch the Bridge Interface toggle to On and then click Continue.

- To enable a WAN PPPoE subinterface, click PPPoE Status and switch the PPPoE Status toggle to on. Note that if you enable PPPoE on a VLAN subinterface of a WAN port, PPPoE is enabled on the other VLAN subinterfaces of the same WAN port by default.
- Click Save.
Add a WAN PPPoE Subinterface on an Activated or Deployed Device
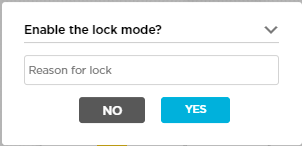
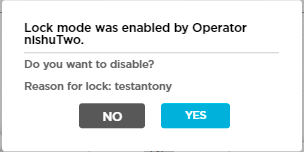
To add a WAN PPPoE subinterface on an activated or deployed device, you first lock the device using the enable lock mode option in the honeycomb view in the Titan Portal home screen. The lock icon displays only if the device is deployed. A blue lock icon indicates that the device is unlocked, and a red red lock icon indicates that the device is locked. After you publish the changes to Titan Portal, you then unlock the device.
To add WAN PPPoE subinterface on an activated device:
- Click Configure in the left menu bar to open the Configure dashboard.
- Click the
 Lock icon in the honeycomb to lock the device.
Lock icon in the honeycomb to lock the device. - Enter a reason for enabling lock mode in the Enable lock mode popup window, and then click Yes.
- Hover over the device in the honeycomb, and click Configure to open the site information window.

- Click the WAN box to open the Network > WAN screen.

- Repeat Step 16 in Create a Site with WAN Subinterface.
- Click Publish and then click Continue.

- Click the
 icon in the honeycomb to unlock the device, and then click Yes.
icon in the honeycomb to unlock the device, and then click Yes.
Configure a Remote Access VPN
For customers who purchase a device license that enables the Versa endpoint client feature in the branch devices and HA devices, you can configure a remote access VPN.
After you add a device, you can enable remote access VPN when configuring the WAN network, and then the Remote Access VPN tab is displayed in the device configuration window.

The Remote Access VPN tab has the following options:
- Versa Endpoint Client Profiles—The Versa endpoint client and SSL VPN profile configuration are common for both the organization and gateway, and is read-only in device view. You configure the Versa endpoint client and SSL VPN profile in the Versa endpoint client default template.
- IPsec Tunnel Address Pool—For a device on which remote access VPN is enabled, select this option to manually enter the WAN IPsec tunnel address pool information.
Before you enable remote access VPN for a device, you must configure an endpoint client service template. For more information, see Configure an Endpoint Client Service (Remote Access VPN) Template.
Use the toggle switch to enable or disable remote access VPN, and then enter the device fully qualified domain name (FQDN). For remote access VPN, you must configure at least one port on the device with a static IP address, which is used to terminate the remote clients.
To configure a remote access VPN:
- In the Add Device Details popup window, click Remote Access VPN toggle to enable the option. See Add Devices Using Titan Portal.
- Configure the endpoint client default template. See Configure an Endpoint Client Service (Remote Access VPN) Template.
- In the Network > WAN window, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Remote Access VPN Interface Click the toggle switch to enable or disable remote access VPN. FQDN Enter the FQDN of the device. Network Address - Address
Enter a static IP address to use to terminate the remote clients. - Gateway
Enter the IP address of the gateway. Name Servers (DNS) - Primary
Enter the IP address of the primary DNS name server. - Secondary
Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS name server. - Deploy the device, or publish if the device is already activated.
- Activate the device, and wait until the device is completely up and the monitor shows a device with an IP address.
- To configure the IPsec tunnel address pool WAN interfaces, select IPsec the Tunnel Address Pool tab, and enter information for the following fields.
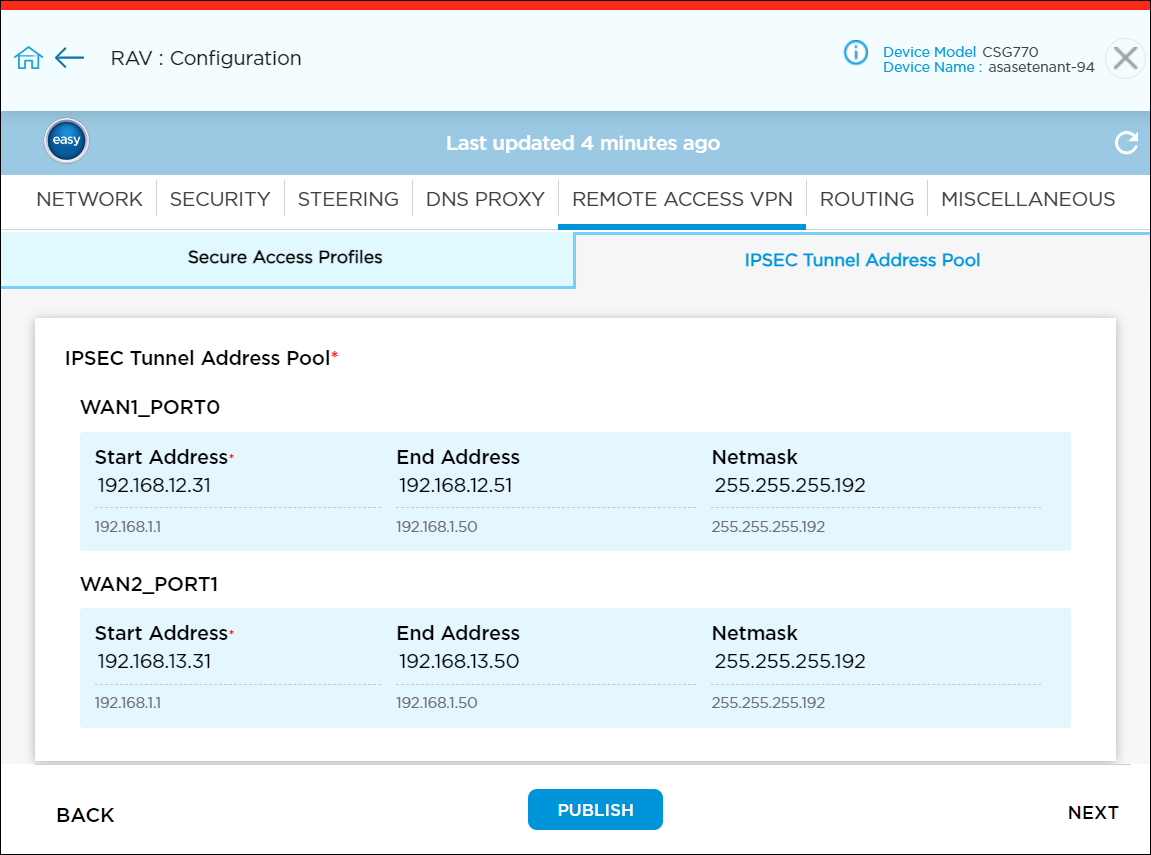
Field Description Start Address Enter the lowest IP address in the pool assigned to the VSA client. End Address Automatically assigned based on the lowest address. Netmask Automatically assigned based on the lowest address. - Upload all necessary key certificates and CA certificate for the device. You can upload a CA certificate only on an activated device. See Configure and Activate SASE Gateway Devices.
- For a new device, configure the captive portal for all WAN ports with the following port numbers. See Configure Miscellaneous Parameters.
- HTTP—80
- HTTPS—443
Edit WAN or LTE Interfaces in an Active Device
After you configure WAN interfaces and deploy or activate the device, you can make the following changes to a WAN or LTE interface:
- Add or remove a WAN, LAN, or LTE interface.
- Switch gateway ON or OFF.
- Update the transport from internet to MPLS or vice versa.
- Enable or disable PPPoE.
To make changes to a WAN or LTE interface, you must first lock the device using the enable lock mode option in the honeycomb view in the Titan Portal home screen. The lock icon displays only if the device is deployed. A blue lock icon indicates that the device is unlocked, and a red lock icon indicates that the device is locked. After you publish the changes to Titan Portal, you must unlock the device.
To edit WAN interfaces:
- Click Configure in the left menu bar to open the Configure dashboard.
- Click the
 icon in the honeycomb to lock the device.
icon in the honeycomb to lock the device. - Enter a reason for enabling lock mode in the Enable lock mode popup window and click Yes.

- Hover over the device in the honeycomb and click Configure to open the site information window.

- Click Next to open the Configuration > Network screen.
- Click the WAN box to open the Network > WAN screen.

- Click WAN1-Port0 to display a list of available ports and their corresponding WAN numbers.
- Select a WAN port.
- Click the
 icon to delete the selected WAN.
icon to delete the selected WAN. - Click the + WAN icon to add a WAN interface. The + WAN icon displays only if WAN ports are available to be configured.
- Click the
- Click Publish and then click Continue.

- Click the
 icon in the honeycomb to unlock the device and then click Yes.
icon in the honeycomb to unlock the device and then click Yes.

Configure IPsec VPN Settings
To create an IPsec tunnel to other appliances or applications, you use the IPsec VPN option on the Network > WAN screen. Titan Portal then adds the name of the tunnel to the drop-down menus for WAN static IP routes, steering rules, and firewall rules for route-based IPsec profiles. For policy-based and rule-based VPNs, no zone or menu options are available in static, steering, and security rules. Tunnels use preshared key (PSK) authentication and are built using IKEv1, IKEv2, or both IKEv1 or IKEv2. If you configure the tunnel using IKEv1, ensure that the shared key value for the local authentication and peer authentication are the same.
When you configure IPsec route-based profiles, by default, Titan Portal creates a security rule that allows IPsec traffic and the rule is displayed in the security rule list. For an IPsec profile, the security rule is created with the same name as IPsec route-based profile name. You cannot edit or delete a system-generated default rule for port forwarding or for an IPsec profile. However, you can disable or reorder a default rule to change its priority.
You can click + Add to configure multiple tunnels.
Note: To enable routing over an IPsec tunnel, you must add a static route towards the tunnel.
To configure an IPsec tunnel:
- From the Network > WAN screen, click the IPsec VPN option to display the IPsec VPN fields.

- In the IPsec VPN option drop-down menu, enter information for the following fields.
Field Description Name Enter the IPsec tunnel name. Titan Portal adds the tunnel name to the IPsec drop-down menu in the Static IP Route screen. Redistribute Click to make the IPsec tunnel eligible for redistribution into the VPN network when thee tunnel is used as the next hop for a static route. VRF Select a source VRF (routing instance). Peer Type Enter format for the peer value: hostname, fully qualified domain name (FQDN), or IP address. Peer Type Value Enter peer value using the format selected in Peer Type. Local Authentication - Authentication Type
Displays the authentication type (PSK). - Identity Type
Enter format for the identity type value: email, FQDN, or IP address. - Identity Type Value
Enter value in the format selected in Identity Type. - Shared Key
Enter preshared key. Peer Authentication - Authentication Type
Displays the authentication type (PSK). - Identity Type
Enter format for the identity type value: email, FQDN, or IP address. - Identity Type Value
Enter value in the format selected in Identity Type. - Shared Key
Enter the preshared key. IKE Version Select the IKE version:
- IKEv1
- IKEv2
- IKEv1 or IKEv2
- Hash Algorithm
Select the hash algorithms to use:
- MD5—MD5 Message Digest Algorithm
- SHA-1—Secure Hash Algorithm 1 with 160-bit digest
- SHA-256—Secure Hash Algorithm 2 with 256-bit digest
- SHA-384—Secure Hash Algorithm 2 with 384-bit digest
- SHA-512—Secure Hash Algorithm 2 with 512-bit digest
- Encryption
Select the encryption algorithms to use:
- 3DES—Triple DES encryption algorithm
- AES 128—AES CBC Encryption Algorithm with 128-bit key
- AES 256—AES CBC Encryption Algorithm with 256-bit key
- DH Group
Select the Diffie-Hellman group to use:
- Diffie-Hellman Group 1—768-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 2—1024-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 5—1536-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 14—2048-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 15—3072-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 16—4096-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 19—256-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 20—384-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 21—521-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 25—192-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 26—224-bit elliptic curve
- IKE Rekey Time
Enter the time interval for how often to regenerate the IKE key.
Range: 3600 through 28800 seconds
Default: 3600 secondsIPsec Transforms Specify the IPsec transform and Diffie-Hellman group. - Hash Algorithm
Select the hash algorithms to use:
- MD5—MD5 Message Digest Algorithm
- SHA-1—Secure Hash Algorithm 1 with 160-bit digest
- SHA-256—Secure Hash Algorithm 2 with 256-bit digest
- SHA-384—Secure Hash Algorithm 2 with 384-bit digest
- SHA-512—Secure Hash Algorithm 2 with 512-bit digest
- XCBC—Extended Cypher Block Chaining
- Encryption
Select the encryption algorithm to use:
- 3DES—Triple DES encryption algorithm
- AES128—AES CBC encryption algorithm with 128-bit key
- AES128-CTR—AES counter mode encryption algorithm with 128-bit key
- AES128-GCM—AES GCM encryption algorithm with 128-bit key
- AES256—AES CBC encryption algorithm with 256-bit key
- AES256-GCM—AES GCM encryption algorithm with 128-bit key
- NULL
- Perfect Forward Secrecy Group
Select the Diffie-Hellman groups to use for PFS:
- Diffie-Hellman Group 1—768-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 2—1024-bit modulus.
- Diffie-Hellman Group 5—1536-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 14—2048-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 15—3072-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 16—4096-bit modulus
- Diffie-Hellman Group 19—256-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 20—384-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 21—521-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 25—192-bit elliptic curve
- Diffie-Hellman Group 26—224-bit elliptic curve
- No PFS
- IPsec Rekey Time
Enter the time interval for how often to regenerate the IPsec key.
Range: 3600 through 28800 seconds
Default: 3600 secondsTunnel Network (Route-Based Only) Use a route-based tunnel configuration. - Tunnel IP Local Address
Enter the IP address of the local tunnel interface in CIDR format. If you do not specify a value, the IP address is automatically generated. - Tunnel IP Remote Address
Enter the IP address of the remote tunnel interface. If you do not specify a value, the IP address is automatically generated. Policy-Based VPN Click the Policy-Based VPN toggle to turn on VPN policies configuration options. If you select this option, click the
 Add Rule icon to add a policy. You can configure a tunnel either using route-based or policy-based options.
Add Rule icon to add a policy. You can configure a tunnel either using route-based or policy-based options.

In the Policy-Based VPN popup window, enter information for the following fields.

- Name—Enter a name for the policy.
- Protocol—Select a protocol:
- Any
- ICMP
- TCP
- UDP
- Source IP—Enter the IPv4 source address or prefix.
- Port—Enter the source port number.
- Destination IP—Enter the IPv4 destination address or prefix.
- Port—Enter the destination port number.
- Click Add.
To change the IPsec tunnel type from a route-based tunnel to a policy-based tunnel, or vice versa, you must delete the existing IPsec tunnel and then publish the configuration. Then, add the IPsec tunnel with required tunnel type, and publish the configuration again. - Click +Add IPsec Profile. This saves the tunnel to the IPsec VPN screen but not the Titan cloud.
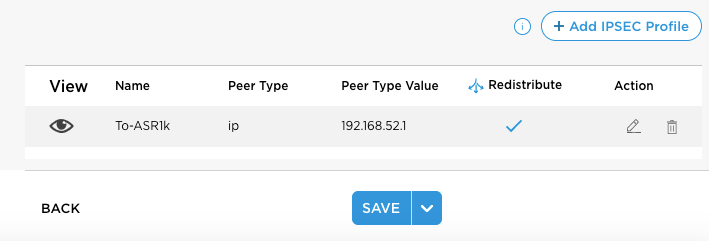
Use the trash icon to delete a tunnel or the pencil icon to edit a tunnel. Click the Eye icon to display tunnel details.
Eye icon to display tunnel details. - Click Save to save the changes to the Titan cloud. Once saved, Titan Portal adds the IPsec tunnel name to the drop-down menus for WAN static IP routes, steering rules, and firewall rules. See Manage Firewall Policies, Configure Traffic Steering, and Configure Internet Traffic Steering.
Configure PPPoE Settings
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is used with DSL services in which individual users connect to a DSL modem over Ethernet. The PPPoE username and password configured on the WAN interface must match settings on the WAN server to be active; otherwise, PPPoE is inactive. You cannot remove or add a new PPPoE instance once a device has been deployed but you can edit the PPPoE username and password at any time.
When PPPoE is active, you can monitor status within the WAN interface from the Monitoring > Network screen. You can also perform a speed test and view steering options from the Speed Test and Steering screens.
Versa Titan supports xDSL interface on CSG355 and CSG365 appliances. You must upgrade these appliances to Versa Operating SystemTM VOSTM (VOS) Release 21.2.1 or later to get the xDSL option displayed in your Versa Titan Portal. GZTP and WiFi are not available for xDSL activation with static IP and PPPoE. Use Versable activation with mobile app to activate the device when xDSL with static IP and PPPoE is configured. You can configure and enable PPPoE only on WAN1 and WAN2 ports before you deploy the device. You use Titan Portal to configure and deploy xDSL device. Titan Mobile can be used only for xDSL device activation and monitoring the status.
To configure PPPoE:
- Click Configure in the left menu bar to open the Configure dashboard.
- Hover over the device in the honeycomb and click Configure to open the site information window.
- Click Next to open the Configuration > Network screen.
- Click the WAN icon and select the WAN interface.
- Click the PPPoE tab and switch the PPPoE Status toggle to on.

- Select an interface type:
- Ethernet
- xDSL
- Select a multiplexing type:
- LLC
- VC-MUX
- Select an instance type in the drop-down menu:
- Internet Only—Traffic is directed to DIA only.
- SD-WAN Only—Traffic is directed to the SD-WAN VPN only.
- SD-WAN and Internet (DIA) Split Tunnel—VPN traffic is directed to the SD-WAN VPN. Internet traffic is directed to DIA.
- Enter the username and password in the fields provided.
- Enter the Service Name provided by DSL provider.
- Enter the name of the access concentrator. The access concentrator name on both the client and the server must be the same to establish the PPPoE session.
- Enter the virtual path identifier.
Range: 0 through 256 - Enter the Virtual channel identifier.
Range: 32 through 65535; 0 through 31 are reserved - Enter the VLAN ID configured for the xDSL line.
- Click Save to save the settings.
Supported Software Information
Releases 11.2 and later support all content described in this article.
