Configure User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) uses machine learning and advanced analytics to detect abnormal user activities in a network. Versa UEBA is a cloud service that provides a layer of security that enables your organization to monitor, detect, and respond to suspicious behaviors across your network infrastructure. Unlike security measures that focus on known attack signatures, UEBA continuously monitors and learns from user interactions, which helps security teams to identify anomalies in real-time and respond proactively to threats.
UEBA Workflow
The UEBA service involves multiple Versa components. You configure UEBA profiles and policies through Versa Concerto, which sends the information to the UEBA service through Versa Director and the configuration server. The SASE gateway shares user activity data with Versa Analytics, which sends the relevant logs to the UEBA service through Kafka.
The UEBA service processes these logs using intelligent algorithms to analyze user activity, and assigns a severity score to each activity. Activity scores are aggregated to compute the overall user confidence score for each user connected to the gateway. Users are assigned to a confidence band based on their scores. The user-to-confidence mapping is sent to the Versa Messaging Service (VMS), which connects to multiple SASE gateways through gRPC.
The confidence score can be used in security access policies. If the confidence score meets a predefined threshold, the relevant security policy profile is applied. For instance, a user might be blocked if the confidence score falls within a specific risk category, such as suspicious. The confidence bands are: high-risk, suspicious, moderate-risk, low-risk, and trustworthy.
The communication between VMS and UEBA cluster (Analytics) is through a Kafka connection for which VMS acts as a client and UEBA is the Kafka server. A Kafka cluster, which is based on open source standards, supports boot strap and broker node types.
Configure UEBA
To configure UEBA, you do the following:
- Configure UEBA profiles from Versa Concerto—You can use predefined profiles or configure custom profiles.
- Configure UEBA policy rules.
Configure UEBA Profiles
The UEBA service allows a combination of predefined and custom profiles that you can associate with the policies of a tenant. You can configure custom profiles if you do not want to use the predefined profiles. In a profile, you define parameters for the user activities that you want to monitor, such as bulk delete, bulk download, bulk upload, and bulk failed logins.
To configure a UEBA profile:
- Go to Configure > Advanced Security > User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) > Profiles.

The following screen displays.

- Click the
 Add icon to create a new UEBA profile. The following screen displays.
Add icon to create a new UEBA profile. The following screen displays.

- Click Behavior Type, and select one of the following types:
- Bulk Delete—Monitor potentially risky users for any malicious activity that would cause data loss due to bulk delete.
- Bulk Download—Identify suspicious download activity from applications and instances where corporate data is stored.
- Bulk Upload—Detect suspicious data movement to applications and sites which could potentially expose corporate data.
- Bulk Failed Logins—Identify attempts to breach corporate user accounts.
- Impossible Travel—Detect geographically distant login activities such as, login attempts by the same user from distant locations that are practically impossible to travel across with in the duration of multiple login attempts. For example, two login activities from the same user within 10 minutes from two geographic locations that are 1000 miles apart.
- Risky Countries—Detect user activity from potentially compromised or infected devices by identifying activity on applications and sites hosted in risky countries.
- (For Releases 12.2.2 and later.) MITRE ATT&CK—Use MITRE Adversarial Tactics, Techniques and Common Knowledge (ATT&CK) to identify and categorize the tactics, techniques and procedures that attackers use during a cyber attack. The MITRE ATT&CK Matrix framework is a globally accessible knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world cyber threat intelligence.
- Enter information for the following fields, which are based on the behavior type that you select in the previous step. Note that the fields are different if you select MITRE ATT&CK for Behavior Type. The following screen displays for other types.

Field Description Count of Files
Enter the number of counts for each behavior type. Based on the value for Behavior Type, the field name changes, and you enter the values for behavior type calculation:
- For Bulk Delete, enter the number of files in Count of Files Deleted.
- For Bulk Download, enter the number of files in Count of Files Downloaded.
- For Bulk Upload, enter the number of files in Count of Files Uploaded.
- For Bulk Failed Logins, enter the number of logins in Count of Failed Logins.
- For Risky Countries, select the countries from Countries.
- For Impossible Travel, enter the number of files in Count of Files.
Value: 0 through 65535.
Time Interval and Unit Type Enter the time interval to count each behavior type based on the Unit Type (Minutes, Hours, or Days).
Value based on Unit Type:
- Minutes—2 through 1440
- Hours—1 through 24.
- Days—1 through 365.
Sensitivity Enter the sensitivity count for each behavior type activity, with 1 being the highest sensitivity and 5 the lowest. Severity Select the severity value for the behavior type:
- Critical
- High
- Informational
- Low
- Medium
- (For Releases 12.2.2 and later.) For MITRE ATT&CK, the following screen displays.

- Select a domain from Company Domain. The options are:
- All
- Government and Diplomatic Entities
- Transportation and Aviation
- Manufacturing
- Defense Industry
- Energy and Critical Infrastructure
- Financial Sector
- Retail and Hospitality
- Technology and Telecommunications
- Education and Academic Institutions
- Healthcare
- Media and News Outlets
- Gaming
For more information, see the MITRE ATT@CK Matrix website.
- To read more information about each MITRE ATT@CK Matrix enterprise or technique, click the
 Info icon next to each item. For example:
Info icon next to each item. For example:
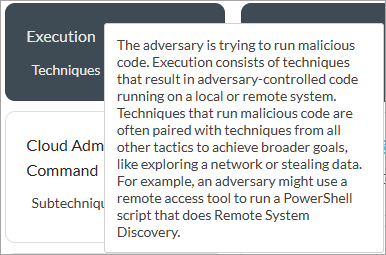
- To select the severity for a sub-technique, click the sub-technique and select a severity that displays on the right side. The severities are Critical, High, Medium, Low, and Informational.
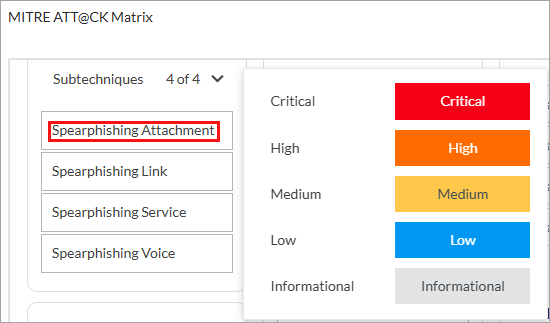
When you select a severity, the sub-technique is highlighted in the color associated with the severity. For example, for Critical the color is red:

- Select a domain from Company Domain. The options are:
- Click Next. In the Review and Submit screen, review the entries you made. To change an entry, click the
 Edit icon and make the change.
Edit icon and make the change.

- In the General section, enter a name for the UEBA profile and, optionally, a description and tags.
- To update the profile behavior, click the
 Edit icon under Behavior Type.
Edit icon under Behavior Type. - For all other sections, review the information. If you need to make changes, click the
 Edit icon.
Edit icon. - Click Save.
Configure UEBA Policy Rules
To configure a UEBA policy rule:
- Go to Configure > Advanced Security > User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) > Policy Rules.
The Policies screen displays.

- To customize which columns display, click Select Columns, and then click the columns to select or deselect the ones that you want to display. Click Reset to return to the default column display settings. The options are:
- Applications
- Users
- Security Enforcement
- Description
- Enabled
- Click the
 Add icon to create a new UEBA policy rule. The Create UEBA Rule screen displays. By default, all applications are selected.
Add icon to create a new UEBA policy rule. The Create UEBA Rule screen displays. By default, all applications are selected.

- Select the applications to include in the policy rule:
- To select a predefined application, click the box for the application. You can use the search function to find specific applications.
- To add a new application, click
 Add New.
Add New.
- Click Users and Groups. By default, all users are selected.

- To specify which users to include in the policy rule, click Customize. The Users and Groups window displays with the User Groups tab selected by default.

- Select one or more user groups to include in the policy rule.
- Click the Users tab, and select one or more users to include in the policy rule.
- Click the Next. In the Security Enforcement tab, select enforcement actions as desired. Note that you must select at least one security enforcement action:
- Bulk Delete—Monitor potentially risky users for any malicious activity that would cause data loss. Enter Count of Files Deleted, Time Interval, and Unit Type; select Sensitivity and Severity.
- Bulk Download—Identify suspicious download activity from applications and instances where corporate data is stored. Enter Count of Files Downloaded, Time Interval, and Unit Type; select Sensitivity and Severity.
- Bulk Upload—Detect suspicious data movement to applications and sites which could potentially expose corporate data. Enter Count of Files Uploaded, Time Interval, and Unit Type; select Sensitivity and Severity.
- Bulk Failed Logins—Identify attempts to breach corporate user accounts. Enter Count of Failed Logins, Time Interval, and Unit Type; select Sensitivity and Severity.
- Impossible Travel—Detect geographically distant login activities. For example, login attempts by the same user from distant locations in a short time.
- Risky Countries—Detect user activity from potentially compromised or infected devices by identifying activity on applications and sites hosted in risky countries.

- Click Review and Deploy and review the entries. Click the
 Edit icon in each section to make changes, if desired.
Edit icon in each section to make changes, if desired.

- In the General section, enter a name for the UEBA rule and, optionally, a description and tags.
- For all other sections, review the information. If you need to make changes, click the Edit icon.
- Click Save.
Publish Tenant UEBA Configuration
After you configure UEBA profiles and policy rules for a tenant, you publish advanced security cloud (ASC) information, which shares the UEBA details to the configuration manager and the clusters that listen to the configuration manager, including the UEBA cluster. The publish information goes from the Concerto node to the Director node, and then to the configuration manager.
To publish the tenant UEBA configuration:
- Click Publish on the top of the UEBA profiles or policy rules screen.
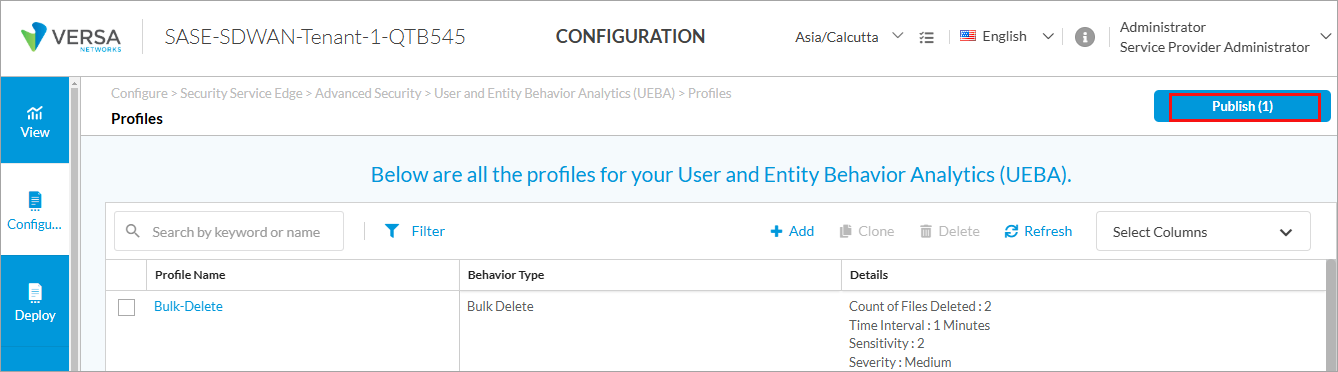
- Select Advanced Security Cloud and click Publish. For more information, see Publish SASE Gateways.
Supported Software Information
Releases 12.2.1 and later support all content described in this article, except:
- Release 12.2.2 adds support for the MITRE ATT&CK behavior type in UEBA profiles.
