Configure CGNAT
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
Carrier-grade NAT (CGNAT) is a large-scale approach to network address translation (NAT). CGNAT translates multiple private IPv4 addresses to a limited number public IPv4 addresses, or private IPv6 addresses to public IPv6 addresses, using network address and port translation (NAPT) methods. In CGNAT, only port translation of the source address is required for packets communicating from the network to outside.
CGNAT can replace NAT on devices in enterprise networks. Using CGNAT, you can deliver seamless IPv4 connectivity even while using limited public addresses. You can define private IPv4 addresses in your network and use Versa CGNAT to manage address translation to the public IPv4 addresses.
To configure CGNAT, you define the address pool to translate and the rules, or criteria, to use for address translation. There are two types of address translation, NAT and NAPT.
For Releases 22.1 and later, you can configure NAT64, to translate IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses, and vice versa, and DNS64, to allow an IPv6-only client to initiate communications by name to an IPv4-only server.
For Releases 22.1.3 and later, you can configure network obfuscation to hide the actual IP address of a server. To allow network obfuscation to work, when you configure a CGNAT address pool, you create a dynamic IP address–only pool, which allocates dynamic destination NAT (DNAT) IP addresses. In response to a client's DNS request, the VOS device advertises an IP address allocated from the dynamic IP address pool to the client instead of the DNS server's actual IP address. The VOS device also creates a dynamic DNAT binding between the allocated dynamic destination IP address and the actual IP address of the DNS server using an endpoint-independent filtering (EIF) entry and gateway. For more information, see Configure a DNS Proxy.
Configure CGNAT Address Pools
You configure address pools to use for CGNAT. For each pool, you define the IP address and port ranges to use, as well as other parameters for the pool.
To configure a CGNAT address pool:
- In Director view:
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Templates > Device Templates in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select an organization in the Organization field.
- Select a template in the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > CGNAT in the left menu bar. The main pane displays the CGNAT pools that are already configured.

- Click the
 Add icon to add a pool. The Add CGNAT Pool popup window displays.
Add icon to add a pool. The Add CGNAT Pool popup window displays. - Select the General tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name Enter a name for the pool. Description Enter a text description for the pool. Tags Enter tags to help identify the pool. Referenced Outside NAT (For Releases 22.1.3 and later.) Click to create a dynamic pool of destination IP addresses. Enable this option when you configure network obfuscation. For more information, see Configure a DNS Proxy. Timeout (Group of Fields) - ICMP
Enter the ICMP mapping timeout, in seconds.
Range: 30 through 3600 seconds
Default: None
- TCP
Enter the TCP mapping timeout, in seconds.
Range: 240 through 10800 seconds
Default: None
- UDP
Enter the UDP mapping timeout, in seconds.
Range: 1 through 3600 seconds
Default: None
- Select the IP address tab to define the IP addresses or IP address range for NAT. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description IP Address/Range (Group of Fields) Click to configure IP addresses and ranges. - IP Address/Mask List
Click the
 Add icon to configure one or more IP addresses and masks. Click the
Add icon to configure one or more IP addresses and masks. Click the  Parameterize icon to parameterize this field so that the field receives its value from bind data.
Parameterize icon to parameterize this field so that the field receives its value from bind data.
IP Address Range (Group of Fields) - Range Name
Enter a name for the IP address range. - Low
Enter the lowest IP address in the range, or click the  Parameterize icon to parameterize this field.
Parameterize icon to parameterize this field.- High
Enter the highest IP address in the range, or click the  Parameterize icon to parameterize this field.
Parameterize icon to parameterize this field. Add icon
Add icon
Click the Add icon to add the IP address range. Note that you can configure multiple IP address ranges, each with a unique name.
Egress Network Click to use one or more egress networks. Click the
 Add icon, and then select a network name in the list.
Add icon, and then select a network name in the list.

Egress Interface Click to use one or more egress networks. Click the
 Add icon, and then select an interface name in the list.
Add icon, and then select an interface name in the list.
Address Allocation Scheme Select the address allocation scheme to use. Routing Instance Select the routing instance to use, or click the  Parameterize icon to parameterize this field.
Parameterize icon to parameterize this field.Provider Organization Select the provider organization to which the CGNAT pool belongs, or click the  Parameterize icon to parameterize this field.
Parameterize icon to parameterize this field. - Select the Port tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Destination Port (Group of Fields) Click to configure the NAT destination port. - Low Port
Enter the lowest port number in the range.
Range: 1 through 65535
Default: None
- High Port
Enter the highest port number in the range.
Range: 1 through 65535
Default: None
Source Port (Group of Fields) Click to configure the NAT source port. - Allocation Scheme
Select the allocation scheme to be used for source port allocation: - Allocate port from range
- Automatic ports assignment
- Low Port
When the allocation scheme is to allocate ports from a range, enter the lowest port number of the range.
Range: 1 through 65535
Default: None
- High Port
When the allocation scheme is to allocate ports from a range, enter the highest port number of the range.
Range: 1 through 65535
Default: None
- Allocate IP/Port Randomly
Select to allocate the IP addresses or port numbers randomly. - Block Reserved Ports
(For Releases 22.1.4 and later.) Select to block reserved ports from the ports allocated for source NAT if the CGNAT pool is address-based.
- Exclude Port Range (Group of Fields)
(For Releases 22.1.3 and later.) Click to exclude a range of source ports. - Low Port
Enter the lowest port number in the range.
Range: 1 through 65535
Default: None
- High Port
Enter the highest port number in the range.
Range: 1 through 65535
Default: None
- Click OK.
Configure CGNAT Rules
You configure the rules to define the criteria to use for address translation.
To configure CGNAT rules:
- In Director view:
- Select the Administration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Appliances in the left menu bar.
- Select a device name in the main panel. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > CGNAT in the left menu bar.

- In the main pane, select the Rules tab in the horizontal menu bar. The main pane displays the rules that are already configured.
- Click the
 Add icon to configure a rule. The Add CGNAT Rule popup window displays.
Add icon to configure a rule. The Add CGNAT Rule popup window displays. - Select the General tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name Enter a name for the CGNAT rule. Description Enter a text description for the CGNAT rule. Tags Enter a keyword or phrase that allows you to filter the CGNAT rule. Tags are useful when you have many rules and want to view those that are tagged with a particular keyword. Precedence Enter a value for the priority of the rule. You can configure multiple rules and assign each a priority. A rule or rules with a higher priority value take precedence over rules with a lower priority value.
Range: 0 through 255
Default: 1Paired Site Click to enable a paired site. For more information, see Configure Paired CPE Devices and Location IDs. - Select the Match tab, and then select the Source tab to configure the criteria to select source traffic for translation. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Source Zones
Click the  Add icon and then select the source zone to match. You can select up to 4 source zones.
Add icon and then select the source zone to match. You can select up to 4 source zones. IP Address/Mask
Click the  Add icon and then select the source IP address prefix to match. You can select up to 16 address prefixes.
Add icon and then select the source IP address prefix to match. You can select up to 16 address prefixes.Routing Instance
Select the routing instance. IP Address Range (Group of Fields)
Enter the source IP address range to match. You can enter up to 16 address ranges.
Note that the IP Address Range and IP Address/Mask options are mutually exclusive.- Range Name
Enter a name for the IP address range. - Low
Enter the lowest IP address in the IP address range. - High
Enter the highest IP address in the IP address range. Protocol
Enter the protocol value to apply to the source traffic. - Select the Destination tab to configure the criteria to select destination traffic for translation. Enter information for the following fields.


Field Description Destination Zones
Click the  Add icon, and then select a destination zone to match. You can select up to 4 zones.
Add icon, and then select a destination zone to match. You can select up to 4 zones.IP Address/Mask
Click the  Add icon, and then select the destination IP address prefix to match. You can select up to 16 address prefixes.
Add icon, and then select the destination IP address prefix to match. You can select up to 16 address prefixes.
Note that the IP Address/Mask and IP Address Range options are mutually exclusive.Destination Interface/Network
Click to select either a destination interface or a destination network to match. Low Port
Enter the lowest port number.
Range: 0 through 65535
Default: None
High Port
Enter the highest port number. Range: 0 through 65535
Default: None
IP Address Range (Group of Fields)
Enter the destination IP address range to match. You can enter up to 16 address ranges.
Note that the IP Address Range and IP Address/Mask options are mutually exclusive.- Range Name
Enter a name for the IP address range. - Low
Enter the lowest IP address in the IP address range. - High
Enter the highest IP address in the IP address range. Protocol
Enter the protocol value to apply to the destination traffic.
Range: 0 through 255
Default: None
- Select the Action tab to define the action to take on the traffic that meets the matching criteria. Enter information for the following fields.
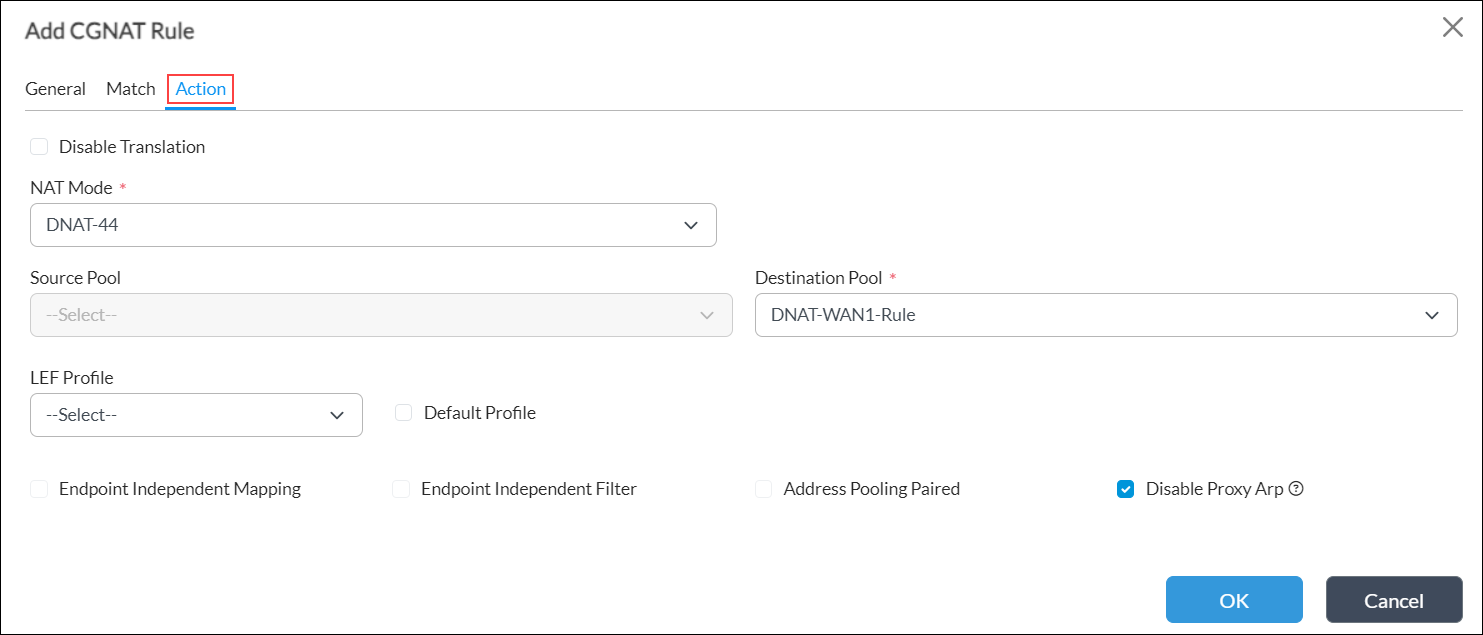
Field Description Disable Translation Click to disable address translation. NAT Mode Select the NAT mode to use to translate private IPv4 addresses to public IPv4 addresses, or private IPv6 addresses to public IPv6 addresses. Network address and port translation methods aggregate multiple private IPv4 addresses into fewer public IPv4 addresses.
- Basic NAT-44—Translate source IPv4 addresses statically.
- DNAT-44—Translate IPv4 destination addresses statically.
- Dynamic NAT-44—Translate only source IPv4 addresses by dynamically choosing the NAT address from the source address pool.
- NAPT-44—Translate the transport identifier (that is, the source IP address) of an IPv4 private network to an IPv4 external address (that is, a public source IP address). Note that you can configure more than one public source addresses in a CGNAT address pool.
- Twice Basic NAT-44—Translate the IPv4 source and destination addresses statically.
- Twice Dynamic NAT-44—Translate the IPv4 source address by dynamically choosing the NAT address from the source address pool and translate the destination address statically.
- Twice NAPT-44—Translate the transport identifier of an IPv4 private network to a single IPv4 external address and translate the destination address statically.
- NPT-66—Translate the transport identifier of the IPv6 private network to a single IPv6 external address.
- NAT-64—Translate IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses, and vice versa. For more information, see Configure NAT64 and DNS64, below.
Source Pool Select the source pool to associate with the translation mode. Destination Pool Select the destination pool to associate with the translation mode. LEF Profile Select the log export functionality profile to use for logging. Use either this field or the default profile field to associate a LEF profile with the CGNAT configuration. For information about configuring a LEF profile, see Configure Log Export Functionality. For information about associating a LEF profile to the configuration of a feature or service, see Apply Log Export Functionality. Default Profile Click to use the default LEF profile. Endpoint-Independent Mapping For the Dynamic NAT-44 and NAPT-44 NAT modes, click to enable endpoint-independent mapping, which NAT uses to perform translation for the duration of the session. Endpoint-Independent Filter For the Dynamic NAT-44 and NAPT-44 NAT modes, click to enable endpoint-independent filtering. Endpoint-independent filtering checks only the destination IP address and destination port of an inbound packet sent by an external endpoint when deciding whether to pass the packet.
Address Pooling Paired For the Dynamic NAT-44 and NAPT-44 NAT modes, click to enable paired address pooling. Use this option for applications that require that all sessions associated with a single internal IP address to be mapped to the same external IP address for the duration of a session.
Disable Proxy ARP (For Releases 22.1.3 and later.) Click to disable automatic proxy ARP installation for the following static NAT modes for IPv4 traffic: - Basic NAT-44
- DNAT-44
- Twice Basic NAT-44
- Twice Dynamic NAT-44
- Twice NAPT-44
By default, proxy ARP is enabled. You can disable proxy ARP if you want to manually configure proxy ARP. To manually configure proxy ARP for an IP address or IP address range configured in CGNAT rules, see Configure Interfaces.
- Click OK.
Configure CGNAT for IPv6
To configure CGNAT for IPv6, you configure Network Prefix Translation-66 (NPTv6). For Releases 22.1 and later, you can also configure Network Address Translation-64 (NAT64) and Domain Name System-64 (DNS64).
Configure NPTv6
Network Prefix Translation (NPTv6) is a stateless, transport-agnostic IPv6-to-IPv6 function that provides the address-independence benefit associated with IPv4-to-IPv4 NAT (NAPT44). NPTv6 also provides a one-to-one relationship between addresses in the prefixes inside the edge network and outside the edge network, preserving end-to-end reachability at the network layer.
NPTv6 is an algorithmic translation in which the checksum remains the same even after the source NAT operation is performed. To compensate for changes to the address prefixes, checksum-neutral values are used for the remainder of the address bits.
It is recommended that you configure NPTv6 CGNAT pools that use prefixes smaller than /48.
To configure NPTv6:
- In Director view:
- Select the Administration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Appliances in the left menu bar.
- Select a device name in the main panel. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > CGNAT in the left menu bar.
- In the main pane, select the Pools tab in the horizontal menu bar. The main pane displays the pools that are already configured.

- Click the + Add icon. The Add CGNAT Pool popup window displays.

- Select the General tab, and then enter information for the following fields.
Field Description Name Enter a name for the pool. Description Enter a text description for the pool. Tags Enter tags to help identify the pool. Referenced Outside NAT (For Releases 22.1.1 and later.) Click to create a dynamic pool of destination IP addresses. Enable this option when you configure network obfuscation. For more information, see Configure a DNS Proxy. Timeout (Group of Fields) - ICMP
Enter the ICMP mapping timeout, in seconds.
Range: 30 through 3600 seconds
Default: None
- TCP
Enter the TCP mapping timeout, in seconds.
Range: 240 through 10800 seconds
Default: None
- UDP
Enter the UDP mapping timeout, in seconds.
Range: 1 through 3600 seconds
Default: None
- Select the IP Address tab.

- Click IP Address/Range, click the
 Add icon, and then enter the IPv6 address range to use for the pool.
Add icon, and then enter the IPv6 address range to use for the pool. - In the Address Allocation Scheme field, select Round Robin.
- In the Routing Instance field, select a routing instance.
- Click OK.
- In the main CGNAT pane, select the Rules tab in the horizontal menu bar. The main pane displays the rules that are already configured.

- Click the
 Add icon. The Add CGNAT Rule popup window displays.
Add icon. The Add CGNAT Rule popup window displays.

- Select the General tab, and then enter information for the following fields.
Field Description Name Enter a name for the CGNAT rule. Description Enter a text description for the CGNAT rule. Tags Enter a keyword or phrase that allows you to filter the CGNAT rule. Tags useful when you have many rules and want to view those that are tagged with a particular keyword. Precedence Enter a value for the priority of the rule. You can configure multiple rules and assign each a priority. A rule or rules with a higher priority value take precedence over rules with a lower priority value.
Range: 0 through 255
Default: 1Paired Site Click to enable a paired site. For more information, see Configure Paired CPE Devices and Location IDs. - Select the Match tab, and then select the Source tab to configure the criteria to select source traffic for translation.

- Click the
 Add icon in the IP Address/Mask table, and then enter the source IPv6 address.
Add icon in the IP Address/Mask table, and then enter the source IPv6 address. - Select the Action tab.

- In the NAT Mode field, select NPT-66.
- In the Source Pool field, select the source pool to use.
- In the LEF field, select the LEF profile to use.
- Click OK.
Configure NAT64 and DNS64
For Releases 22.1 and later.
NAT64 and DNS64 allow you to configure basic services, such as firewall and DDoS rules, with originating IPv6 addresses and zones. Translated IPv4 packets can be routed over SD-WAN networks, paired TVI interfaces, or tunnel interfaces.
NAT64, defined in RFC 6146, provides a mechanism to translate IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses, and vice versa. The IPv4 destination address in the forward direction is derived from the IPv4-embedded IPv6 address in the IPv6 destination address field, as specified in RFC 6052. This IPv6 destination address is resolved by DNS64, as described below, with support for the prefix lengths /32, /40, /48, /56, /64, and /96. The IPv6 source addresses of IPv6 hosts are translated to and from IPv4 addresses by installing mappings in the normal Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) source NAT pool, and they adhere to the source NAT configurations for the NAPT pool.
DNS64, defined in RFC 6147, allows an IPv6-only client to initiate communications by name to an IPv4-only server. DNS64 is a mechanism for synthesizing AAAA resource records (RRs) from A RRs. A synthetic AAAA RR created by DNS64 from an original A RR contains the name of the owner of the original A RR, but it contains an IPv6 address instead of an IPv4 address. The IPv6 address is an IPv6 representation of the IPv4 address contained in the original A RR. The IPv6 representation of the IPv4 address is algorithmically generated from the IPv4 address returned in the A RR and a set of parameters configured in DNS64.
The only shared states between DNS64 and the NAT64 translator are the Pref64::/n keyword and an optional set of static parameters. You must configure the same keyword and parameters on both devices. There is no communication between the DNS64 device and NAT64 translator functions.
The following example shows how to configure NAT-64:
- In Director view:
- Select the Administration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Appliances in the left menu bar.
- Select a device name in the main panel. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > CGNAT in the left menu bar.
- In the main pane, select the Rules tab in the horizontal menu bar. The main pane displays the rules that are already configured.
- Click the
 Add icon. The Add CGNAT Rule popup window displays.
Add icon. The Add CGNAT Rule popup window displays.

- Select the General tab, and then enter a name for the rule in the Name field.
- Select the Match tab.

- Select the Source tab. The IP Address/Mask is not required. You can enter ::/0 to include all IPv6 addresses.
- Select the Destination tab, click the
 Add icon, and then enter the IPv6 address and mask in the IP Address/Mask field.
Add icon, and then enter the IPv6 address and mask in the IP Address/Mask field.

- Select the Action tab. and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description NAT Mode Select NAT-64. DNS64 Prefix Enter the DNS64 prefix. Source Pool Select the source pool. -
Click OK.
Supported Software Information
Releases 20.2 and later support all content described in this article, except:
- Release 22.1 adds support for NAT64 and DNS64.
- Release 22.1.3 adds support for disabling proxy ARP, dynamic DNAT, and exclude a range of source ports.
- Release 22.1.4 adds support for blocking reserved ports.
