Configure Network Obfuscation
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
You can configure network obfuscation to hide the internal network topology and remote Versa SASE clients from each other. With network obfuscation, you obscure the physical resource hosting the application (that is, the server IP address) from end users, thus helping to secure devices against attack vectors, such as port scanning and lateral movement.
You can enable the following types of network obfuscation:
- Remote user obfuscation—For remote Versa SASE clients. Obfuscates all Versa SASE client IP addresses from the remote servers.
- Application obfuscation—For private applications. When you enable application obfuscation, you select the VPN instance name as the traffic source and one or more private applications. The selected applications are made intentionally unclear for all the tenant's users regardless of how they access gateways, that is, whether they are using the Versa SASE client, SD-WAN, or site-to-site tunnels. You can also create a group of applications to exclude from obfuscation.
You can also configure a DNS proxy with network obfuscation for the Versa SASE client.
Configure Network Obfuscation
To configure network obfuscation:
- Go to Configure > Security Service Edge > Real-Time Protection > Network Obfuscation.

- To enable remote user obfuscation, select the Remote User Obfuscation tab, and then slide the toggle to Enabled.

- Click Save.
- To enable obfuscation for an application, select the Application Obfuscation tab, and then slide the toggle to Enabled.
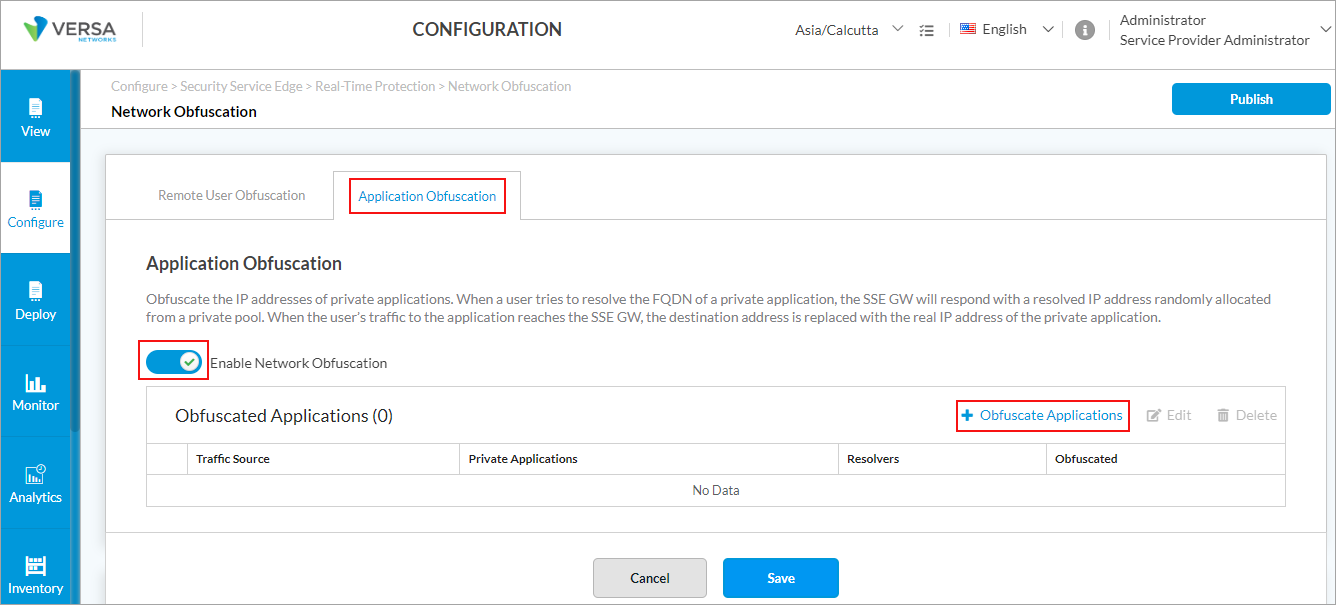
- Click + Obfuscation Applications.
- In the Obfuscate Applications screen, enter information for the following fields.
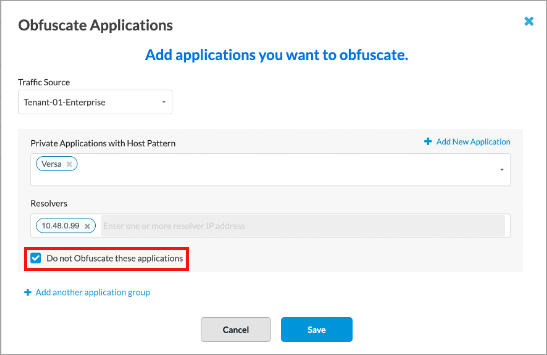
Field Description Traffic Source Select the VPN instance as the traffic source. Private Applications Select one or more private applications. To add a new application, click + Add New Application. The Application screen displays. For more information, see Configure SASE Private Application Protection Rules.
Resolvers Enter one or more DNS server resolver IP addresses for the private applications. Do Not Obfuscate These Applications Click to exclude the private applications you selected from obfuscation. - Click + Add Another Application Group to create another group of private applications with different resolvers or a different obfuscation choice. For more information, see Configure SASE Private Application Protection Rules.
- To add a private application, click + Add New Application. The Application screen displays.
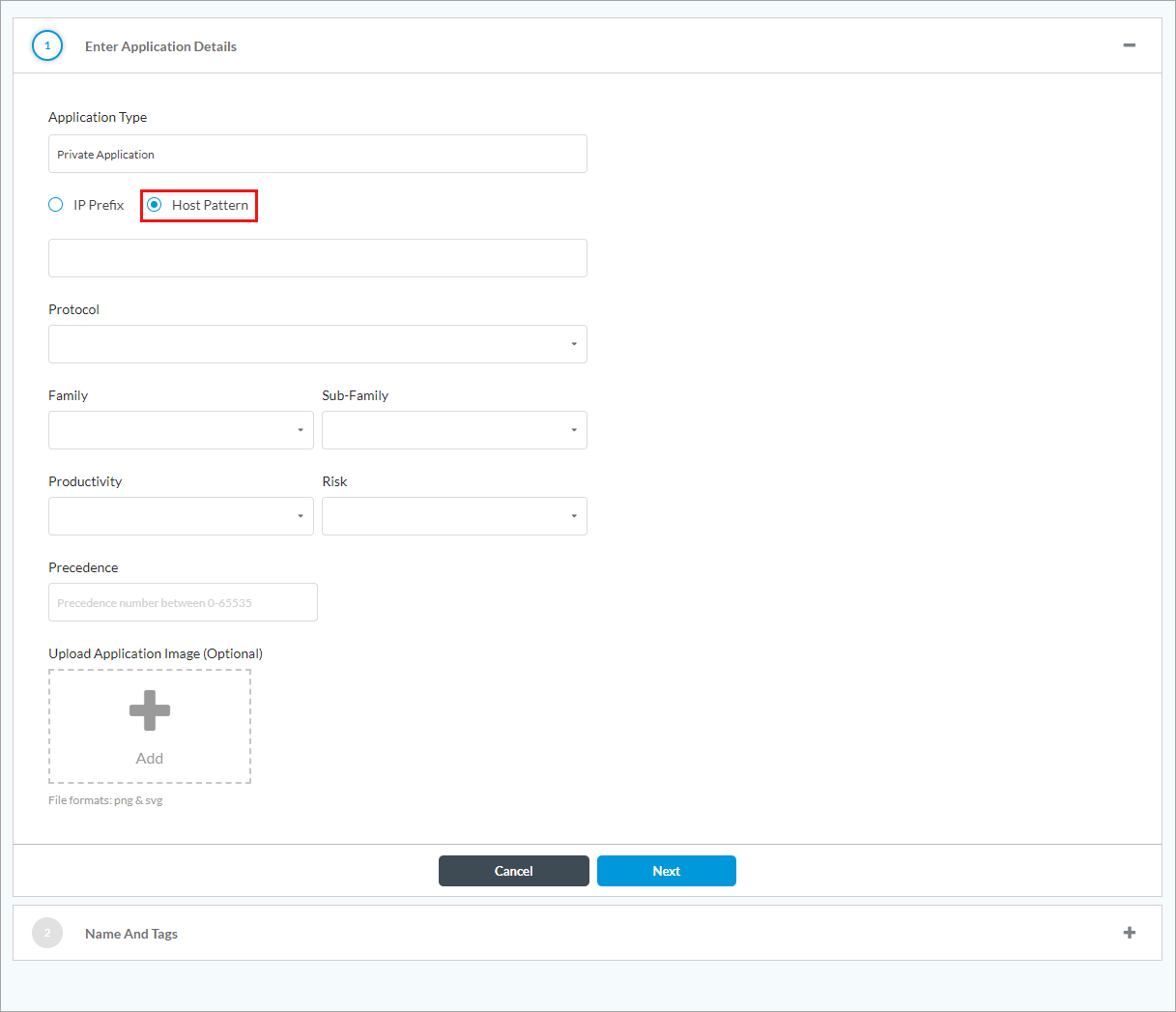
- Select Host Pattern. Note that only applications with a configured host pattern are displayed in the Private Applications field in the Obfuscate Applications window. Applications with a configured IP prefix are not displayed.
- For information about configuring other parameters, see Configure SASE Private Application Protection Rules.
- Click Add. The Application Obfuscation dashboard displays the configuration for each set of private applications.

- Click Save.
Example: Configure DNS Proxy Using Network Obfuscation
This example explains how to configure a DNS proxy with network obfuscation for Versa SASE client when the client receives its global DNS setting from Versa SASE gateway. When the SASE gateway receives a DNS request for a specified domain, it intercepts the request and forwards it to the configured internal DNS server. All other domains are resolved using the global DNS server.
The following are scenarios for using DNS proxy with network obfuscation for the SASE client:
- DNS Proxy for a specific domain—Your organization may have internal applications or services that require customized DNS handling. For example, you might need to resolve certain domains to local servers, apply specific security filters, or route traffic through a dedicated DNS service. In such cases, you can configure selective DNS requests to be forwarded through DNS proxy to the corporate DNS. All other external DNS queries, such as those for websites or cloud services, can be sent to the global DNS server for standard resolution.
- Protect private DNS settings—Your organization may prefer not to push private DNS settings to end clients. Instead, once the traffic reaches the gateway, DNS requests can be proxied to the corporate DNS for resolution and monitoring. In this scenario, the DNS proxy intercepts and forwards all relevant requests to the corporate DNS.
Verify Gateway Receives Global DNS Settings
In this example, the client connects to the SASE gateway, VERSA-SASE-GW-02-003, and the client is configured with global DNS setting 8.8.8.8.
To verify if the client is connected to the SASE gateway and receives global DNS settings (for Window OS):
- From command prompt, run the ipconfig /all CLI command.
- Under PPP adapter for the tenant gateway (here, tenant-01-VERSA-SASE-GW-02-003), check DNS Servers. In the example below, the client is configured with DNS set to 8.8.8.8:
C:\Users\user>ipconfig /all Windows IP Configuration WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . . . : No DNS Suffix Search List. . . . . . . . : versa-networks.com PPP adapter tenant-01-VERSA-SASE-GW-02-003: Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : Description . . . . . . . . . . . : tenant-01-VERSA-SASE-GW-02-003 Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : No Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.10.3(Preferred) Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.255 Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 0.0.0.0 DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 8.8.8.8 NetBIOS over Tcpip. . . . . . . . : Enabled
Configure Network Obfuscation for a Domain
Next, configure network obfuscation for the domain for which DNS requests must point to the internal DNS server.
- In the Obfuscate Applications screen, enter the required details. For more information, see Configure Network Obfuscation above.

In this example, the traffic originates from Tenant-01-Enterprise, and the SASE gateway, configured with the Versa Networks domain, forwards the request to an internal server for resolution. - Click Do not Obfuscate these Applications.
- Click Save.
- To verify how DNS requests are processed for external and internal domains, run the nslookup CLI command from the command prompt. For example, the following screenshot shows the DNS details for Facebook and for an internal Wiki:
C:\Users\user1> nslookup facebook.com Server: dns.google Address: 8.8.8.8 Non-authoritative answer: Name: facebook.com Addresses: 2a03:2880:f137:182:face:b00c:0:25de 157.240.192.35 C:\Users\user1>nslookup wiki.<wiki-name>.com Server: dns.google Address: 8.8.8.8 Name: wiki.<wiki-name>.com Address: 192.0.2.1
Monitor DNS Proxy Statistics
To view DNS proxy statistics:
- Click Monitor > Devices and select the gateway.
- Click Networking > DNS Proxy. For example:

Supported Software Information
Releases 11.4.1 and later support all content described in this article.
Releases 7.8.11 of Versa SASE Client and later support all content described in this article.
Additional Information
Configure SASE Private Application Protection Rules
Configure SASE User-Defined Objects
