Configure Profile Elements
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
You use the Configure lifecycle to create all configuration objects for Secure SD-WAN deployments. The Concerto configuration objects are hierarchical. For more information, see Configuration Hierarchies.
The top level of the hierarchy consists of Profiles and Profile Elements. The Profiles hierarchy consists of Master Profiles and Subprofiles. For information about configuring profiles, see Configure Profiles.
Profile elements are reusable configuration objects that are part of all profiles. There are four types of profile elements:
- Policies—You can configure the following types of policies for a profile element:
- Application
- Device Policies
- Network Services
- Security
- User and Device Authentication
- Routing
- VPN
- System
- Policy elements—You can configure the following types of policy elements for a profile element:
- Device
- Network services
- VPN elements
- Rules—You can configure the following types of rules for a profile element:
- Application
- Security
- Elements—You can configure the following types of elements for a profile element:
- Application
- Certificates
- Endpoint
- Monitor
- Security (for Releases 12.1.1 and later.)
- QoS
- Servers
- VPN name
Add New Profile Elements
To add a new profile element:
- In Tenants view, select the tenant name. The configured landing page for the tenant displays.
- In the left menu bar, click Configure. The Configure screen displays, and the Profiles tab is selected.
- Select the Profile Elements tab, and then navigate to the type of profile element that you want to create. For example, to create a new Radio device policy, you would navigate as follows: Configure > Profile Elements > Policies > Device Policies > Radio.

The following screen displays.

- Click + Radio. The Create Radio Policy screen displays.

- Enter the required information in the General, Radio, and Permissions tabs.
- Click Save.
Add New Application Elements
You can configure the following types of new application elements to use in higher-level policies and subprofiles:
- Custom Application
- Predefined Application (for Releases 12.2.1 and later.)
- Application Category (for Releases 12.2.1 and later.)
- Application Group
- Application Classification
- Forwarding Profile
- TCP Optimizations
Add Custom Application Elements
To add a custom application element:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Application > Custom Application.

The Applications screen displays all created custom applications and a horizontal menu bar.

- In the horizontal menu bar, you can select one of the following operations.

Operation Description Add Create a new custom application. This button is active when no existing application is selected. Clone Clone the selected application. In the Clone popup window, enter a name for the custom application and, then click Submit.

Delete Delete the selected custom application. A popup window similar to the following displays:

Click Yes to delete the application, or click No to retain the application.
Refresh Refresh the list of existing custom applications. - To customize which columns to display, click Select Columns and then click the columns to display or hide. Click Reset to return to the default column settings.
- In the Applications screen, click the
 Add icon to add a custom application.
Add icon to add a custom application. - In the Add Applications screen, Select Step 1, Match Criteria. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description IP Prefix Click to use an IP prefix. Then enter a valid IP prefix and subnet. Note that if you select IP Prefix, you cannot also select Host Pattern. Host Pattern Click to use a host pattern. Then enter a host pattern to detect. Note that if you select Host Pattern, you cannot also select IP Prefix. Protocol Select a protocol. If you selected Host Pattern, TCP is the only protocol available. Source Port If you select IP Prefix and either TCP or UDP, enter the source port number. You can enter a single port value or a range of value,; for example, 500 and 1-100.
Range: 0 through 65535
Default: None
Destination Port If you select IP Prefix and either TCP or UDP, enter the destination port number. You can enter a single port value or a range of values, for example, 500 and 1-100.
Range: 0 through 65535
Default: None
Precedence (For Releases 11.4.1 and later.) Enter a unique priority number to use when multiple applications match the traffic. The application with a higher precedence value is matched first.
Range: 0 through 65535
- Click Next to go to Step 2, Application Attributes. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Risk Select a risk level. Each application has been assessed and assigned a risk level by the Versa Networks security research team, as follows:
- Level 1—Lowest Risk
- Level 2—Low Risk
- Level 3—Medium Risk
- Level 4—High Risk
- Level 5—Highest Risk
Productivity Select a productivity level. Each application has been assessed and assigned a productivity level by the Versa Networks security research team, as follows:
- Level 1—Lowest Productivity
- Level 2—Low Productivity
- Level 3—Medium Productivity
- Level 4—High Productivity
- Level 5—Highest Productivity
Family Select a family to associate with the application. Subfamily Select a subfamily to associate with the application. Application Tags—Security (For Releases 12.2.1 and later.) Select one or more security tags to associate with the application. Application Tags—SD-WAN (For Releases 12.2.1 and later.) Select one or more SD-WAN tags to associate with the application. Application Tags—General (For Releases 12.2.1 and later.) Select one or more general tags to associate with the application. - Click Next to go to Step 3, Permissions, and then revise the permissions if necessary.

- Click Next to go to Step 4, Review and Submit. In General section, enter information for the following fields. Then review the information and edit them if needed.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the custom application. Description (Optional) Enter a description for the application. Tags (Optional) Enter one or more tags to to associate with the application. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no spaces or special characters that you use for searching objects. Upload Application Image (Optional) Click the  Add icon. In the popup window, select an application image and upload it. Images must be in .png or .svg format.
Add icon. In the popup window, select an application image and upload it. Images must be in .png or .svg format. - Click Save.
View Predefined Applications
For Releases 12.2.1 and later.
To view predefined applications:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Application > Predefined Application.

- To view predefined applications, select the Predefined Internet Applications tab.
Note: In Release 12.2.1 and later, deprecated predefined applications are not displayed. If you had already configured a rule in Releases 12.1.1 and earlier that included a now-deprecated application in its match criteria, and then try to edit that rule, an error message similar to the following is displayed.


- To edit an application, click the application in the Application column.
- In the Edit Predefined Internet Applications screen, make the required changes and then click Save.

- In the Confirm popup window, click Save. The modified applications are listed in the User Modified Predefined Internet Applications tab.

- To view user-modified predefined internet applications, select the User Modified Predefined Internet Applications tab.

Add Application Category Elements
For Releases 12.2.1 and later.
Custom application categories are used to match information based on the attributes of predefined or custom applications. Versa Networks currently provides 4,763 predefined applications.
For each category, you can create one or more filters:
- Application Risk—Each application has been assessed and assigned a risk level (1 through 5, lowest to highest) by the Versa Networks security research team.
- Application Productivity—Each application has been assessed and assigned a productivity level (1 through 5, lowest to highest) by the Versa Networks security research team.
- Application Tags—You can configure up to three types of application tags:
- Security
- SD-WAN
- General
- Application Family and Subfamily—You can select any of five application families and 34 application subfamilies.
You can use application categories when you configure application policies and rules, such as policies and rules for QoS and traffic steering.
To configure an application category:
- Go to Configure > Secure SD-WAN > Profile Elements > Elements > Application > Application Category.

The following screen displays.

- To customize which columns display, click the
 Select Columns down arrow, and then select or deselect the columns you want to display. Click Reset to return to the default column settings. The options are:
Select Columns down arrow, and then select or deselect the columns you want to display. Click Reset to return to the default column settings. The options are:
- Risks
- Productivity
- Family
- Sub Family
- Security
- SD-WAN
- General
- Click the
 Add icon to configure a new application category. The Add Application Categories screen displays Step 1, Settings.
Add icon to configure a new application category. The Add Application Categories screen displays Step 1, Settings.

As you select categories, the application list adjusts to only show the applications that match selected categories. For example, in the sample screen above, 4,763 predefined applications and 61 user-defined applications are selected. Because no filters have yet been configured, these numbers represent the total number of predefined and user-defined applications that are available. The numbers change as you configure the various application filters. If you select multiple filters, the list changes to display the applications that match all of the filters you selected.
- To customize the application risk filter, click the
 Chevron icon next to Application Risk, and then select one or more application risk filters.
Chevron icon next to Application Risk, and then select one or more application risk filters.

In this example screen, two risk levels are selected: Level 4 and Level 5. There are 152 Level 4 (high risk) applications and 138 Level 5 (highest risk) applications, for a total of 290 applications. This total matches the sum of the numbers displayed in the Predefined Applications (282) and User Defined Applications (8) tabs.
- To customize the application productivity filter, click the
 Chevron icon next to Application Productivity, and then select one or more application productivity filters.
Chevron icon next to Application Productivity, and then select one or more application productivity filters.

In this example screen, one productivity level is selected: Level 4. There are 152 Level 4 (high productivity) applications. Of these 152 applications, 34 match the combined filter criteria of Level 4 and Level 5 application risk plus Level 4 application productivity. This total matches the sum of the numbers displayed in the Predefined Applications (30) and User Defined Applications (4) tabs. - To customize the application tags filter, click the
 Chevron icon next to Application Tags, and then select one or more application tag filters.
Chevron icon next to Application Tags, and then select one or more application tag filters.

In this example screen, one application security tag is selected. There are 10 predefined applications and 1 user-defined application, for a total of 11 applications that match all of the selected filters. This total matches the sum of the numbers displayed in the Predefined Applications (10) and User Defined Applications (1) tabs. - To customize the application family and sub-family filter, click the
 Chevron icon next to Application Family and Sub-Family, then select one or more filters.
Chevron icon next to Application Family and Sub-Family, then select one or more filters.

In this example screen, one application family tag is selected. There are 10 predefined applications and 1 user-defined application, for a total of 11 applications that match all of the selected filters. This total matches the sum of the numbers displayed in the Predefined Applications (10) and User Defined Applications (1) tabs. - Click Next.
- In Step 2, Name, Description, and Tags, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the application. Description (Optional) Enter a description for the application. Tags (Optional) Enter one or more tags to to associate with the application. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no spaces or special characters that you use for searching objects. - Click Save to add the application category.
Add Application Group Elements
To add a new application group:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Application > Application Group.

The following screen displays.

- Click + Application Group. The Create Application Group screen displays. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name Enter a name for the custom application. Type Select the custom application type. Internet is the only available type. Logo Add a logo for the custom application. Click the + Add icon to upload an application image, and then select an image and upload it. The image must be in .png or .svg format.
Tags Enter one or more tags. A tag is an alphanumeric descriptor, with no white spaces or special characters that you can use to search the objects. - Select the Applications tab, click in the Search for Applications field, and then select the applications to include in the group.
Note: You can select only internet and predefined applications.

- Select the Permissions tab, and then revise the permissions if necessary.

- Click Save to create the application group.
Add Application Classification Elements
To add a new application classification element:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Application > Application Classification.

- Select Application Classification. The screen displays the application classifications that are already configured.

- Click + Application Classification. The Create Application Classification screen displays.
- Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name Enter a name for the application classification. Forwarding Class (Group of Fields) - Category
Select a category:
- Assured
- Best Effort
- Expedited
- Network
- Class
Select a class. The classes listed depend on the category you select.
- 0 through 3 (for Network category)
- 4 through 7 (for Expedited category)
- 8 through 11 (for Assured category)
- 12 through 15 (for Best Effort category)
- Click Advanced to configure advanced options.

- Select a term, and then enter information for the following fields. Available terms are Loss Priority, Traffic Conditioning, SLA Metrics, and Connection Priority.
Field Description Connection Priority Select a connection type:
- Internet
- LTE
- MPLS
Click Avoid to avoid using the selected connections when forwarding traffic.
Click Add to add the term, or click cancel to cancel the selected connection type.
Loss Priority Select the loss priority:
- High
- Low
SLA Metrics Select an SLA metric:
- Low Latency
- Low Packet Loss
- Low Delay Variation
Traffic Conditioning Select one or more traffic conditions:
- FEC (forward error correction)
- Load Balance—Click the
slider to select per-flow or per-packet load balancing.
- Replication
- Click Advanced again, or click Add Term to add more terms.
- Select the Application Category tab.

- Click Add Category to add more categories.

- In the Name field, enter a name for the application category.
- Click Add Term.
- Add Traffic Conditioning, SLA Metrics, and Connection Priority terms, as described in Step 5 above.
- Select the Members tab.

- Click Add Criteria, and then add the desired criteria. For more information, see Configure QoS Policies and Rules and Configure Traffic-Steering Policies and Rules, above.
- Click Save.
Add Forwarding Profile Application Elements
- Click Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Application > Forwarding Profile.

The Forwarding Profile screen displays all the configured forwarding profiles.

- To customize which columns to display, click Select Columns and then click the columns to display or hide. Click Reset to return to the default column settings.

- To create a forwarding profile, click + Add Forwarding Profile. In the Step 1, Path Selection screen, select a route path type.
- SD-WAN (see steps 4 through 6)
- Direct Internet and/or Preferred Exit Location (see steps 9 through 13)
- Click SD-WAN to select the SD-WAN route path for forwarding traffic, and then enter information for the following fields. Note that in Releases 11.3.2 and earlier, you configure the forwarding profile on a single screen.

Field Description Priority
Select the path priorities based on WAN connection names, types, or remote site names:
- 1 through 8
- Avoid—Configure the path as one to avoid. An avoided path is not used even if it is the only available path. If the only available paths are configured as avoid, traffic is dropped.
- Last Resort—Use the when all other paths are down. As an example, you can configure a last resort so as not to use LTE paths when other paths are available.
Connection Mode
Select the connection mode:
- Name
- Type
Local
If you select the Name WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection name on the local branch:
- Internet-1
- Internet-2
If you select the Type WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection type on the local branch:
- Broadband
- LTE
- MPLS
Remote
If you select the Name WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection name on the remote branch:
- Internet-1
- Internet-2
If you select the Type WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection type on the remote branch:
- Broadband
- LTE
- MPLS
- To add another path with the same priority value, click the
Plus icon. To remove a path within the same priority value, click the
Minus icon.
- To add a path with a different priority value, click Add Priority, and perform Steps 4 and 5.
- Select Connection Priority for Unconfigured Paths.
- Click Direct Internet and/or Preferred SD-WAN Exit Location to select a direct internet preferred exit location route type, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Next-Hop Selection Method Select how to choose the next hop for DIA traffic:
- Automatic—Select the next hop that provides the best performance based on passively collected performance metrics.
- High-Available Bandwidth—Use high-available bandwidth to load-balance DIA traffic among equal priority next hops.
- Load Balance—Perform equal-cost load balancing among all active next hops at the highest priority level using SLA monitoring and SLA-based path selection metrics.
- Weighted Round-Robin—Use WRR to load-balance DIA traffic between equal priority next-hops.
Next-Hop Failure Action Select the action to take when none of the configured next hops is deemed reachable:
- Failover—Fall back to routing-based path selection.
- Next Rule—Fail over to the next matching rule.
- Wait Recover—Wait for this rule to recover at least one next hop.
Session Pinning to DNS Path Slide the toggle button to pin all sessions between a client and server to the path of the DNS query that resolved the server. - Click Next-Hop Priority, and then click Add Route Path. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Priority Select a next-hop priority value.
Range: 1 through 15Path Type Select a path type:
- Preferred SD-WAN Exit Location—Select the traffic path in the SD-WAN VPN network where the next hop or exit location is a branch, gateway, or hub.
- Direct Internet—Select the WAN circuit for internet breakout traffic at the branch.
Preferred SD-WAN Exit Location (Group of Fields) - Exit Location
Select the branch as an exit location. - SLA Monitor
Select the SLA Monitor created under the Monitor. See Configure SaaS Application Monitors. - Maximum Latency
Enter a value for the maximum traffic latency, in milliseconds. - Maximum Packet Loss
Enter a percentage value for the total combined forward and reverse packet loss. Direct Internet (Group of Fields) - WAN Connection
Select the WAN connection.
- Next-Hop Address
Enter the next-hop address. - Reachability Monitor
Select the reachability monitor. - SLA Monitor
Select an SLA nonitor that you created under the Monitor. See Configure SaaS Application Monitors. - Maximum Latency
Enter a value for the maximum traffic latency, in milliseconds. - Maximum Packet Loss
Enter a percentage value for the total combined forward and reverse packet loss. -
Click SD-WAN Path Priority, and then click Add Priority. Enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Priority
Select the path priorities based on WAN connection names, types, or remote site names:
- 1 through 8
- Avoid—Configure the path as one to avoid. An avoided path is not used even if it is the only available path. If the only available paths are configured as avoid, traffic is dropped.
- Last Resort—Use the when all other paths are down. As an example, you can configure a last resort so as not to use LTE paths when other paths are available.
Connection Mode
Select the connection mode:
- Name
- Type
Local
If you select the Name WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection name on the local branch:
- Internet-1
- Internet-2
If you select the Type WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection type on the local branch:
- Broadband
- LTE
- MPLS
Remote
If you select the Name WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection name on the remote branch:
- Internet-1
- Internet-2
If you select the Type WAN connection mode, select a WAN connection type on the remote branch:
- Broadband
- LT
- MPLS
- To add another path with the same priority value, click the
Plus icon. To remove a path within the same priority value, click the
Minus icon.
- To add a path with a different priority value, click Add Priority, and perform steps 3 and 4.
- Click Next. In the Step 2, Service Level Agreement (SLA) screen, enter information for the following fields.
Field Description Maximum Latency Enter a value for the maximum traffic latency (delay). The link latency is a two-way measurement.
Range: 1 to 1000 milliseconds
Default: NoneLow Latency Slide the toggle button to select a path based on the lowest latency. Maximum Jitter Enter a value for the forward and reverse delay variation (jitter).
Range: 1 to 100 milliseconds
Default: NoneLow Jitter Slide the toggle button to select a path based on the lowest delay variation (jitter). Maximum Packet Loss Enter a percentage value for the total combined forward and reverse packet loss.
Range: 1 to 100 percent
Default: NoneLow Packet Loss Slide the toggle button to select a path based on the lowest packet loss. Maximum Transmit Utilization Enter the percentage of a circuit's available bandwidth to use to transmit traffic.
Range: 1 to 100 percent
Default: NoneMaximum Receive Utilization Enter the percentage of a circuit's available bandwidth to use to receive traffic.
<Range: 1 to 100 percent
Default: NoneConnection Selection Method Select how to forward a traffic flow when multiple available WAN paths have the highest priority. For example, if there are two paths at priority 1 and one path at priority 2, one of the priority 1 paths is chosen.
- High available bandwidth—Use the circuit with the highest available bandwidth. Continuing with the example in the previous bullet, because the available bandwidth on WAN2 is higher, this link would be used.
- Path high available bandwidth
- Path weighted round-robin
- Weighted round-robin—Use WRR, which balances flows across paths proportional to their available bandwidth. This is the default connection selection method.
Default: WRR
Recompute Timer Enter how often to re-evaluate the SLA-compliance state of all paths. If the re-evaluation identifies an SLA violation on a circuit, the traffic is switched to a different circuit.
Range: 5 through 1800 seconds
Default: 300 secondsMean Opinion Score (MOS) Enter a mean opinion score for audio, video, and voice traffic. Mean opinion score is a measure of the quality of voice data traffic, and it represents the user experience of audio, video, and voice applications. Voice data is always compressed using a codec before it is transmitted, and so the MOS score can vary for the voice data on the same link depending on the codec.
Range: 0 to 5, where 5 represents the best traffic quality
Default: NoneEnable Gradual Migration Click the  toggle button to enable gradual migration.
toggle button to enable gradual migration.Enable SLA Violation Damping Click the  toggle button to enable gradual migration. Select this option to associate the recompute interval value with the damping interval value. If you do not enable SLA violation damping, the SLA compliance of a path is checked every recompute interval.
toggle button to enable gradual migration. Select this option to associate the recompute interval value with the damping interval value. If you do not enable SLA violation damping, the SLA compliance of a path is checked every recompute interval.SLA Smoothing Interval Enter the SLA smoothing interval, in seconds.
Range: 10 through 300 seconds
Default: 120 secondsSLA Violation Damping Interval Enter the SLA violation damping interval, in seconds.
Range: 10 through 300 seconds
- Click Next. In the Step 3, Path Conditioning screen, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Forwarding Error Correction (FEC) (Group of Fields) - Enable FEC
Click the  toggle button to enable FEC.
toggle button to enable FEC.
Default: Disabled- Send FEC Packet To
Select the circuit on which to send FEC parity packets:
- Alternate circuit—Send FEC parity packets on a WAN interface that is not an interface on which data packets are transmitted. This is the default. If an alternate circuit is unavailable, FEC parity packets are sent on the same circuit as data packets.
- Same circuit—Send FEC parity packets on the same WAN interface used to transmit data packets.
Default: Alternate circuit
- Duplicate FEC Packet
Select how to duplicate FEC parity packets:
- Alternate circuit—Duplicate FEC parity packets and send them on a WAN interface that is not an interface on which data packets are transmitted.
- Disable—Do not duplicate FEC parity packets. This is the default.
- Same circuit—Duplicate FEC parity packets and send them on the same WAN interface used to transmit data packets.
Default: Disable
- Number of Data Packets per FEC Packets
Enter the number of data packets after which an FEC packet is generated and sent to the peer branch. The generated FEC parity packet can recover a packet on the peer branch only if there is one lost packet in the specified number of packets per FEC.
Range: 1 through 32
Default: 4- Start When
Select when to start sending FEC parity packets:
- Always
- SLA violated—When all available paths are SLA violated
- Stop When
Click to set the circuit utilization threshold at which to stop sending FEC parity packets. - Circuit Utilization
When you enable Stop When, enter the utilization threshold at which replication stops automatically. Specify this as a percentage of the total circuit bandwidth. When the circuit utilization of the links used for data packets or FEC parity packet transmission exceeds this threshold, FEC stops.
Range: 1 through 100 percent
Default: NonePacket Replication (Group of Fields) - Enable Packet Replication
Click the  toggle button to enable packet replication.
toggle button to enable packet replication.
Default: Disabled- Replication Factor
For each ingress packet, define the number of egress packets to send.
Range: 2 through 4
- Start When
Select when to start replication automatically:
- Always
- SLA violated—When all available paths do not meet configured SLA threshold
Stop When Click to enable using a circuit utilization threshold value to stop packet replication. Circuit Utilization When you enable Stop When, enter the circuit utilization threshold at which replication stops automatically. Specify this as a percentage of the total circuit bandwidth. When the circuit utilization exceeds this threshold value, packet replication stops automatically.
Range: 1 through 100 percent
Default: None
- Click Next. In Step 4, Permissions screen displays, showing the default roles and their inherited permissions.

- If desired, change the permissions by selecting a new permission level for each role.
- Click Next to go to Step 5, Review and Submit screen.

- In the General section, enter a name for the forwarding profile. Optionally, enter a description and add tags for the profile.
- Click Edit next to any section to make changes.
- Click Save.
Add TCP Optimization Application Elements
For Releases 11.3.1 and later.
TCP optimizations mitigate the effects of high latency and packet loss on the performance of TCP-based applications. The optimizations are based on a TCP proxy architecture in which one or more VOS devices in a network path between a client and server split the TCP connection into two. One connection faces the client and one faces the server, with the VOS devices acting as TCP proxies for each of the split network segments. The optimizations can be done in one of the following modes:
- Dual-ended mode—TCP connection is split between two peer VOS devices in the network path
- Single-ended mode—TCP connection is split independently on one or more VOS devices in the network path
After you create a new TCP optimization application element, you can use it when configuring traffic-steering rules.
To add a TCP optimization application forwarding profile element:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Application.

- Select TCP Optimization Profile. The screen displays already configured TCP optimization profiles.

- Click + TCP Optimization Profile. In the Create TCP Optimization Profile screen, enter information for the following fields.
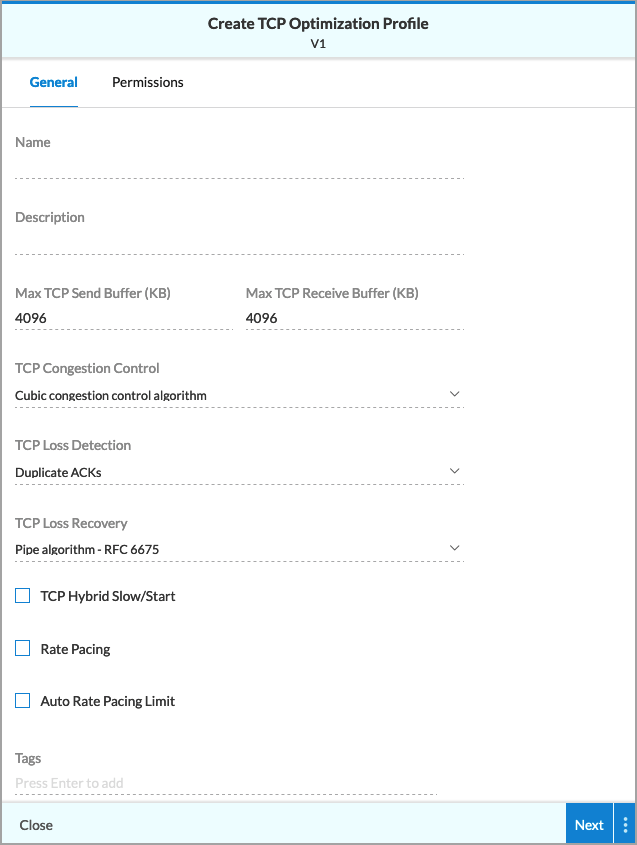
Field Description Name Enter a name for the TCP optimization profile. Maximum TCP Send Buffer Enter the maximum size of the TCP send buffer. Setting the buffer size limits TCP memory consumption.
Range: 64 through 16384 KB
Default: 4096 KBMaximum TCP Received Buffer Enter the maximum size of the TCP receive buffer. Setting the buffer size limits TCP memory consumption.
Range: 64 through 16384 KB
Default: 4096 KBTCP Congestion Control Select the congestion control algorithm to use:
- BBR congestion control algorithm—Bottleneck bandwidth and round-trip propagation time measures both the largest amount of recent bandwidth available to a connection and the connection's smallest recent round-trip delay. BBR then uses these metrics to control how fast it sends data and how much data it allows to be sent at any given time.
- Cubic congestion control algorithm—An algorithm that uses a cubic function instead of a linear window increase function to improve scalability and stability for fast and long-distance networks. This is the default.
- New Reno congestion control algorithm—An algorithm that responds to partial acknowledgments.
Default: Cubic congestion control algorithm.
TCP Loss Detection Select the method to use to detect TCP packet loss:
- Duplicate ACKs—Loss detection based on duplicate acknowledgements. Duplicate acknowledgements mean that one or more packets have been lost in a TCP stream and the connection is attempting to recover them. They are a common symptom of packet loss.
- Recent acknowledgment (RACK). RACK uses the notion of time, instead of packet or sequence counts, to detect losses.
Default: Duplicate ACKs
TCP Loss Recovery Select the method to use to recover lost TCP packets:
- Pipe algorithm—Perform TCP loss recovery as described in RFC 6675. This is the default.
- Proportional rate reduction—Perform TCP loss recovery as described in RFC 6937.
Default: Pipe algorithm
TCP Hybrid Slow/Start Click to enable TCP hybrid slow start. Hybrid slow start maintains the TCP slow-start mechanism, which probes network bandwidth and gradually increases the amount of data transmitted until it finds the network's maximum carrying capacity. It also provides a mechanism to help TCP slow-start to exit without incurring a large number of lost packets. By default, hybrid slow start is disabled.
Default: DisabledRate Pacing Click to enable rate pacing. Rate pacing injects packets smoothly into the network, thereby avoiding transmission bursts, which could lead to packet loss. By default, rate pacing is disabled.
Default: DisabledAutomatic Rate-Pacing Limit Click to enable rate pacing. Rate pacing injects packets smoothly into the network, thereby avoiding transmission bursts, which could lead to packet loss. By default, rate pacing is disabled.
Default: DisabledTags Enter one or more tags. A tag is an alphanumeric descriptor, with no white spaces or special characters, that you can use to search the objects. - Click Next, or select the Permissions tab and update the permissions as needed.
- Click Save.
Reference a TCP Optimization Application Element in a Traffic-Steering Rule
For Releases 11.3.1 and later.
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Rules > Applications > Traffic Steering.

- Click + Traffic Steering.

- In the Create Traffic Steering Rule screen, enter a name for the rule.

- Select the Criteria tab, and the add the desired criteria. For more information, see Configure Traffic-Steering Policies and Rules, above.

- Click the Actions tab, and then enter information for the following fields.


Field Description Type Flow Select the flow type action:
- Allow
- Drop. If you select Drop, no other actions can be taken.
Type Log Under Events, select one of the following:
- Never—Do not send logs.
- Priority Change—Send logs only when the traffic priority changes.
- SLA Violated—Send logs only when the traffic violates the SLA.
Forwarding Profile (Group of Fields) - Name
Enter a name for the forwarding profile. - Term Type
Select a term type:
- Connection Priority
- Path Conditioning
- SLA
- Connection Priority
Create path priorities based on WAN connection names, types, or remote site names. The WAN connection name and type can be local, remote, or both.

- For Path Type Enterprise:
- Connection Mode
- Name—Select Internet-1 or Internet-2 from the first drop-down list, and then select Any (default), Local, or Remote from the second drop-down list.
- Type—Select Broadband, MPLS, or LTE, and then select Any (default), Local, or Remote from the second drop-down list.
- Exit Location—Currently not supported.
- Connection Mode

- For Path Type Direct Internet:
- Name—Select Internet-1 or Internet-2.
- Application Monitor—Select an application monitor.
- Add Connection Mode—Click to add an additional connection mode.
- Avoid—If Guest is enabled, this VPN does not participate in the SD-WAN topology and only Direct Internet Access is provisioned.
- Path Conditioning
Set level of FEC and packet replication:
- Aggressive
- Moderate
- Standard
- SLA
SLA—Select the SLA by criteria or based on absolute metrics.
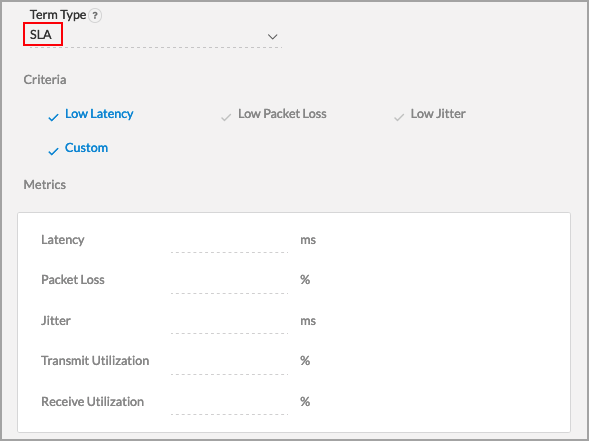
If you select Custom, enter information for the following fields:
- Latency—Enter the amount of latency in milliseconds (ms).
Range: 1 through 1000 milliseconds - Packet Loss—Enter the percentage of packet loss allowed.
- Jitter—Enter the amount of jitter allowed, in milliseconds.
Range: 1 through 100 milliseconds - Transmit Utilization—Enter the percentage of transit traffic.
- Receive Utilization—Enter the percentage of received traffic.
Add Term Click to add additional forwarding profile terms. TCP Optimization Profile (Group of Fields) - Mode
Select the TCP optimization mode:
- Auto—Detect which VOS device is closest to the client and which is closest to the server (peer discovery)
- Bypass—Disable TCP optimizations.
- Forward proxy—Optimize data being sent from clients to servers. You configure this option on the VOS device closer to the client.
- Proxy—Configure a single VOS device to be a proxy for the TCP connection instead of performing end-to-end peer discovery.
- Reverse proxy—Optimizes data being sent from servers to clients. You configure this option on the VOS device closer to the server.
- Splice—Split the TCP connection locally after an application or URL category is identified or when the VOS device receives the first data packet after the three-way handshake completes.
- Bypass Latency Threshold
If you select TCP Auto or Splice mode, enter how much latency must be measured before TCP optimizations begin.
Range: 0 through 60000 milliseconds
Default: 10 milliseconds- LAN Profile
Select a LAN profile.
For proxy mode, you must configure a TCP profile.
Note that you can select the same TCP profile for LAN profiles and WAN profiles.
If you do not select TCP profiles, a system default LAN profile is applied that uses the cubic congestion control algorithm and duplicate ACK loss detection.
- WAN Profile
Select a WAN profile.
For proxy mode, you must configure a TCP profile.
Note that you can select the same TCP profile for WAN profiles and LAN profiles.
If you do not select TCP profiles, a system default WAN profile is applied that uses the BBR congestion control algorithm and RACK loss detection.
- Click Next, or select the Permissions tab and update the permissions as desired.
- Click Save.
Configure Custom SD-WAN Security Profile Elements
For Releases 12.1.1 and later.
You can configure two types of custom SD-WAN profile elements:
- Security actions—Allows you to choose the type of security action (such as cloud access security broker (CASB), decryption, and DNS) and the action to take on that type.
- URL categories—Allows you to create a custom URL category by specifying a URL pattern and reputation, a URL string and reputation, and by uploading files in .csv format.
Note: You can configure URL categories and security actions as part of both SSE and SD-WAN services in Concerto. The configurations are common between the two services. If you configure URL categories and security actions for an SSE service, the same configuration appears in the SD-WAN service, and vice versa.
You can then use the security actions and URL categories when you configure security policies under Configure > Profile Elements > Policies > Security.
Configure Security Actions
To configure a security actions profile element:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Security > Security Actions.

The following screen displays.

- Click + Add Security Actions. The Add Security Actions screen displays.
- Select Step 1, Define Security Action, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Security Action Type Select a security action type:
- All
- CASB
- Decryption
- DNS
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
- IP Filtering
- URL Filtering (URLF)
Action Select an action:
- Allow—Forward the current packet without generating an entry in the log.
- Drop Packet—Browser waits for a response from the server and then drops the packets.
- Drop Sessions—Browser waits for a response from the server and then drops the session.
- Reset Client—TCP Reset packet is sent to the client and the browser displays an error message indicating that the connection has been reset.
- Reset Client and Server—TCP Reset packet is sent to the server. The browser waits for a response from the server and then drops the session.
- Block—Present an alert page to the user and block the user from continuing, in case of HTTP/HTTPS.
- Inform—Browser presents an information page that allows the user to continue with the operation by clicking OK.
- Ask—Browser presents an information page that allows the user to either cancel the operation by clicking Cancel, or continue with the operation by clicking OK.
- Justify—Browser presents an information page that allows the user to either cancel the operation by clicking Cancel, or continue with the operation after entering a justification message and clicking OK.
- Override—Browser prompts the user to enter a PIN (4 to 6 digits).
- Custom Redirection—Browser redirects the user to the URL configured in the Redirection URL field.
- Sinkhole—A DNS sinkhole spoofs DNS servers to prevent the resolution of the host names associated with URLs. And returns a false IP address to the URL, thus blocking a DNS sinkhole.
Decrypt Bypass (For all security types except CASB.) Click the slider bar to disable SSL encryption for matching traffic, to allow you to define web sites that are not subject to decryption. SSL encryption for matching traffic is enabled by default. Log Captive Portal Actions (For all security types except CASB.) Click the slider bar to enable the logging of captive portal actions. Logging of captive portal actions is disabled by default. Expiration Time (For the security types IP Reputation and URL Filtering.) Enter how often to redirect a user to the URL, in minutes. Message (For the security types IP Reputation and URL Filtering.) Enter a message to display on the captive portal page. - Click Next to go to Step 2, Name, Description, and Tags, and then enter information for the following fields.
Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the security action. Description Enter a text description. Tags Enter one or more tags. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no spaces or special characters that you use for searching tunnels. - Click Save.
Configure URL Categories
To configure a URL categories profile element:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > Security > URL Categories.

The following screen displays.

- Click + Add URL Categories.
- In the Add URL Categories screen, select Step 1, URL Patterns, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Patterns Enter a URL pattern to match and group the URLs. You can include regex patterns. For example, you can use the pattern www.versa-networks.com, or you can use a wildcard such as *.versa-networks. To include a backslash (\) in the regex pattern, escape it by preceding it with a backslash.
Reputation Select a predefined reputation, and then assign it to the URL match pattern. - Click Next. In Step 2, URL Strings, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description String Enter a URL string to match the URL, for example, www.versa-networks.com. Reputation Select a predefined reputation, and then assign it to the URL string. - Click Next. In Step 3, URL Files, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description URL Files Select a URL file. Add New File Click to add a new URL file. The Upload File popup window displays.

- Enter the name of the file to upload or click Browse to select the file. The file must be in .csv format
- Click Upload.
- Click Next. In Step 4, Enter Name, Description, and Tags, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the URL category. This name is displayed in the category list when defining the URL-filtering policies and in the match criteria for URL categories in policy rules. Description Enter a text description for the URL category. Tags Enter one or more tags for the URL category. A tag is an alphanumeric text descriptor with no spaces or special characters that you use for searching URL categories. - Click Save.
Create a New VPN
To create a new VPN:
- Go to Configure > Profile Elements > Elements > VPN Name.

The following screen displays.
- Click + VPN Name. In the Create VPN Name screen, enter the following information.

Field Description VPN Name Enter a name for the VPN. Description (Optional) Enter a description of the VPN. Guest (Optional) Click the slider bar to configure the VPN as a guest VPN. A guest VPN does not participate in the SD-WAN topology. Only Direct Internet Access (DIA) is provisioned. -
Click Save to create the new VPN.
Supported Software Information
Releases 10.2.1 and later support all content described in this article, except:
- Release 11.1.1 adds support for the Custom Application and Application Group application elements.
- Release 11.2.1 adds support for multitenancy configuration in Default-Active-Active and Default-Basic-MP basic master profiles, and for a new default basic master subtenant profile, Default-Basic-MP-Sub-Tenant.
- Release 11.3.1 adds support for the TCP optimizations application element and the ability to add service templates to individual devices in a redundant master profile.
- Release 11.4.1 adds support for a configuration wizard for configuring access control policies and rules; the creation of CGNAT rules for subtenants in addition to provider tenants in multitenant master profiles; custom applications support family, subfamily, risk, productivity and precedence; enhanced forwarding profiles and IP SLA profiles.
- Release 12.1.1 adds support for the custom SD-WAN security profile elements Security Actions and URL Categories.
- Release 12.2.1 adds support for predefined applications and application tags for custom applications; deprecated predefined applications are not displayed in the Concerto UI screens.
