Configure Microsegmentation
![]() For supported software information, click here.
For supported software information, click here.
Microsegmentation is a network security strategy that allows you to divide a network into smaller, isolated segments, called microsegments. You create each microsegment around a specific set of resources or services, and you define access controls and configure security policies that are specific for the resources and services in the microsegment. Traditional network security models primarily rely on securing the network perimeter, using methods such as firewalls to protect the entire network. With microsegmentation, you can divide the network into smaller segments and then apply security controls at a more granular level, thus providing an additional layer of security. You can create security zones in your network and apply security policies to each microsegment to provide enhanced security by restricting lateral movement within the network.
With Versa Operating SystemTM (VOSTM) microsegmentation, you can place user client devices and clientless (headless) IoT devices into microsegments.
To create a microsegment, you define a policy whose match criteria place a user or device into the microsegment. Then you apply policies to restrict or allow traffic among microsegments.
In VOS microsegmentation policy rules, you can configure match criteria based on information collected by Versa SASE client-based devices and by clientless devices. For end user client devices that use the Versa SASE client, such as laptops, you can configure endpoint information profiles (EIPs), which periodically provide device (endpoint) information to registered SASE gateways. You can then configure microsegmentation access policy rules that match the EIP data provided by the SASE client, which allows the VOS devices to identify user devices and place them into the proper microsegment. Because the SASE client sends periodic updates, the SASE gateways regularly evaluate client devices. For example, if a microsegmentation policy determines that a device's antivirus software is not up to date, thus making the device vulnerable to attack, it can place the device into a quarantined microsegment to ensure that the device cannot communicate with other users or devices in the network. Then, if the device's antivirus software is upgraded, after the SASE client conveys this information to the first-hop SASE gateway, the microsegmentation policy can move the device into a non-quarantined microsegment.
For headless IoT devices that do not run the Versa SASE client, such as sensors and printers, you use VOS device fingerprinting to identify the device based on its model, vendor, and other associated attributes. You can then configure microsegmentation access policy rules that match the fingerprinting data, which allows the VOS devices to identify user devices and place them into the proper microsegment.
This article describes how to configure microsegmentation policy and rules, associate microsegments with NPU and NGFW policies, and monitor microsegmentation policies and statistics.
Configure Microsegmentation Policies
To create a microsegmentation policy, first you create a policy, and then you create rules to place devices and users in microsegments.
Configure a Microsegmentation Policy
- In Director view:
- Select the Administration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Appliance in the left menu bar.
- Select the device from the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > Next-Gen Firewall > Microsegmentation > Policies in the left menu bar. For more information about enabling NGFW, see Enable NGFW in Configure NGFW.

- In the Policies tab click + Add. In the Add Policies popup window, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the microsegmentation policy. The name, Default-Policy, displays by default, which you can edit. Description Enter a text description for the microsegmentation policy. - Click OK.
Configure Microsegmentation Rules
- In Director view:
- Select the Administration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Appliance in the left menu bar.
- Select the device from the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > Next-Gen Firewall > Microsegmentation > Policies in the left menu bar.

- Select the Rules tab, and then click + Add.
- If you have already added a rule, the Add popup window displays.
- Select where you want to insert the policy rule, either at the beginning or end of the existing rule.

- If there are two or more rules, you can drag the line with the Place Here text to insert the rule where required.

- Click OK. The Add Rules popup window displays.
- Select where you want to insert the policy rule, either at the beginning or end of the existing rule.
- Select the General tab, and then enter Information for the following fields.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the microsegmentation rule. Description Enter a text description for the microsegmentation rule. Disable Rule Click to disable the rule. You can disable a rule to skip it from evaluating traffic and to use other rules in the policy in the configuration order. - Select the Match tab, and then enter information for the following fields.
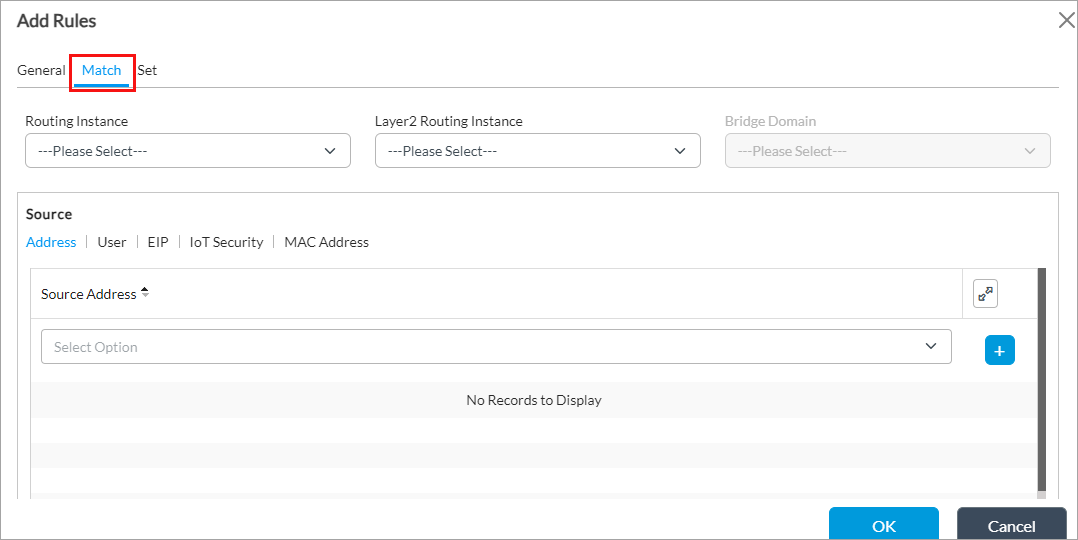
Field Description Routing Instance Select a routing instance on which to match incoming traffic. You can select a router instance or a Layer 2 routing instance, but not both. Layer 2 Routing Instance Select a Layer 2 routing instance of type Virtual Switch. This matches the incoming traffic on the bridge domain you select in the Bridge Domain field. Because a bridge domain is Layer 2, you must configure a virtual switch instead of a virtual router. You can select a router instance or a Layer 2 routing instance, but not both.
Bridge Domain If you select Layer 2 Routing Instance, select a bridge domain for Layer 2 routing instance. - In the Source field, select the Address tab, and then enter information for the following fields.
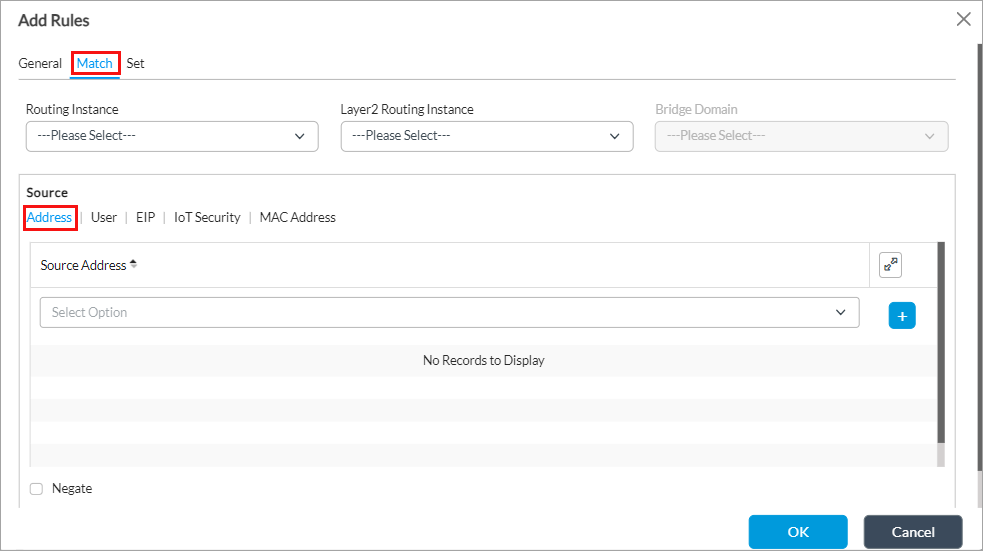
Field Description Source Address Select the one or more source addresses or source address groups of incoming traffic to match, and then click the Add icon.
Negate Click to block traffic to the selected source addresses or groups instead of accepting it. - Select the User tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Match Users Select the users to match. You can select only one option.
- Any—Match any users.
- Known—Match known users.
- Selected—Match selected users.
- Unknown—Match unknown users.
User Group Profile If you match selected users, select a user group profile to match the users in the group. Local Database If you match selected users, click to create a local database to match users and user groups. Select these users and user groups in the Users and Groups fields. For more information, see Configure a Local Database. External Database If you match selected users, click to use an external database to match users and user groups. Select these users in the Users and Groups fields. For more information, see Configure User and Group Policy. Users If you match selected users, select a user and then click the Add icon to add the user.
Groups If you match selected users, select a user group and then click the Add icon to add the group.
- Select the EIP Profiles tab to associate endpoint information profiles (EIPs) with the rule.

- In the EIP Profiles table, select one or more user-defined or predefined EIP profiles, and then click the
Add icon to associate EIP with the rule. With EIPs, you collect information about the security status of the endpoint devices connecting to your networks, such as whether they have the latest security patches and antivirus definitions installed. For more information, see Configure Endpoint Information Profiles.
- Select the IoT Security tab, and then enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Devices Select user-defined or discovered devices to associate with the rule, and then click the
Add icon to add the device. Click + Devices to add an IoT security device. When you enable IoT security, VOS starts to discover and identify devices that enter your network traffic. For more information, see Configure IoT Security.
Device Filters Select user-defined or predefined device filters to associate with the rule, and then click the
Add icon to add a device filter.
Click + Device Filters to add an IoT security device filter. For more information, see Configure IoT Security.
Device Groups Select a IoT device group to associate with the rule, and then click the
Add icon to add a device group. Click + Device Groups to add an IoT security device group. For more information, see Configure IoT Security.
- Select the MAC Address tab to configure match criteria based on source MAC addresses.

- In the MAC Address List table, select a MAC address, and the click the
Add icon.
- Click OK.
- Select the Set tab to select scalable group tags (SGTs) to classify and tag network traffic, and then define security policies to take actions on this traffic.

- In the Scalable Group Tag field, select an SGT. Clients that match the filter criteria are placed in this microsegment for this rule.
- Click OK.
Associate Microsegments with NGFW and NPU Policies
You add match parameters in NPU and NGFW policy rules to match microsegments.
One method to associate a microsegment with an NPU or NGFW rule is to associate the SGT ID used in a microsegmentation rule with an NPU or NGFW rule. For this type of configuration, you do the following:
- Create an SGT object.
- Associate the SGT object with a microsegmentation rule.
- Associate the SGT object with an NPU ACL policy rule or an NGFW security policy rule.
Create an SGT Object
- In Director view:
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Templates > Device Templates in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select an organization in the left menu bar.
- Select a template in the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Objects & Connectors > Objects > Custom Objects > Scalable Group Tag in the left menu bar.

- Click +Add. In the Add Scalable Group Tag popup window, enter information for the following fields.

Field Description Name (Required) Enter a name for the SGT (here, Windows-Devices). Description Enter a text description for the SGT. Tag Number (Required) Enter a tag number.
Range: 0 to 4094
- Click OK.
Associate the SGT with a Microsegmentation Rule
- In Director view:
- Select the Administration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Appliance in the left menu bar.
- Select the device from the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > Next-Gen Firewall > Microsegmentation > Policies in the left menu bar.
- Select the Rules tab and click + Add.
- In the Add Rules popup window, select the Set tab.

- In the Scalable Group Tag field, select the SGT (here, Windows-Devices) that you configured in Create an SGT Object, above.
- For information about configuring other parameters, see Configure Microsegmentation Rules, above.
Associate the SGT with an NPU ACL Policy Rule
In this example, we associate the SGT with a Layer 2 ingress ACL rule. You can associate SGT with Layer 2 IPv4 and IPv6, Layer 3 IPv4 (single wide and double wide), and Layer 3 IPv6 ACL rules. For more information, see Configure NPU Policy-Based Forwarding.
To configure a Layer 2 ingress ACL policy:
- In Director View:
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Devices > Devices in the horizontal menu bar.
- Click the name of an appliance. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Networking > NPU > Layer 2 ACL Ingress in the left menu bar.

- Select the Policies tab, and then click the + Add icon or the + Add button. The Add Rules popup window displays.
- Select the Match tab.

- In the Source SGT ID or Destination SGT ID field, select the SGT (here, Windows-Devices) that you configured in Create an SGT Object, above.
- For information about configuring other parameters, see Configure Layer 2 Ingress ACLs.
- Click OK.
Associate the SGT with an NGFW Security Policy Rule
- In Director view:
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Templates in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select an organization in the left navigation bar.
- Select a template in the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Services > Next-Gen Firewall > Security > Policies in the left menu bar, and then select the Rules tab.

- Click + Add to define rules for the policy. The Add Rule popup window displays.
- Select the Source tab.

- In the Scalable Group Tab field, select the SGT (here, Windows-Devices) that you configured in Create an SGT Object, above.
- For information about configuring other parameters, see Configure Access Policy Rules (ACL Rules) in Configure NGFW.
- To associate the SGT with the destination traffic, select the Destination tab.

- In the Scalable Group Tag field, select the SGT (here, Windows-Devices) that you configured in Create an SGT Object, above.
- Click OK.
Monitor Microsegmentation Policies and Statistics
To monitor a microsegmentation policy:
- In Director view:
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Devices > Devices in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select a device in the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Monitor tab in the top menu bar.
- Select the provider organization in the left menu bar.
- Select the Services tab in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select NGFW > Microsegmentation, and then select the microsegmentation policy. The table displays the rules associated with the microsegmentation policy and the number of times each rule has been used in evaluating traffic.

To view statistics about microsegments:
- In Director view:
- Select the Configuration tab in the top menu bar.
- Select Devices > Devices in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select a device in the main pane. The view changes to Appliance view.
- Select the Monitor tab in the top menu bar.
- Select the provider organization in the left menu bar.
- Select the Services tab in the horizontal menu bar.
- Select NGFW > Microsegmentation Statistics.
- In the first filter field, select Local Statistics, and then select All, IP address, Routing Instance, or Segment in the second filter field. For example:
- Select Local Statistics and All to display all information about a microsegment:

- Select Local Statistics and IP to display IP address information about a microsegment:

- Select Local Statistics and Routing Instance to display routing instance information about a microsegment:

- Select Local Statistics and Segment to display microsegment information:

- Click View in any of the windows to display more details:

- Select Local Statistics and All to display all information about a microsegment:
- To view tunnel details about a microsegement, select Tunnel Statistics in the first filter field and All, which is the only option in the second filter field.
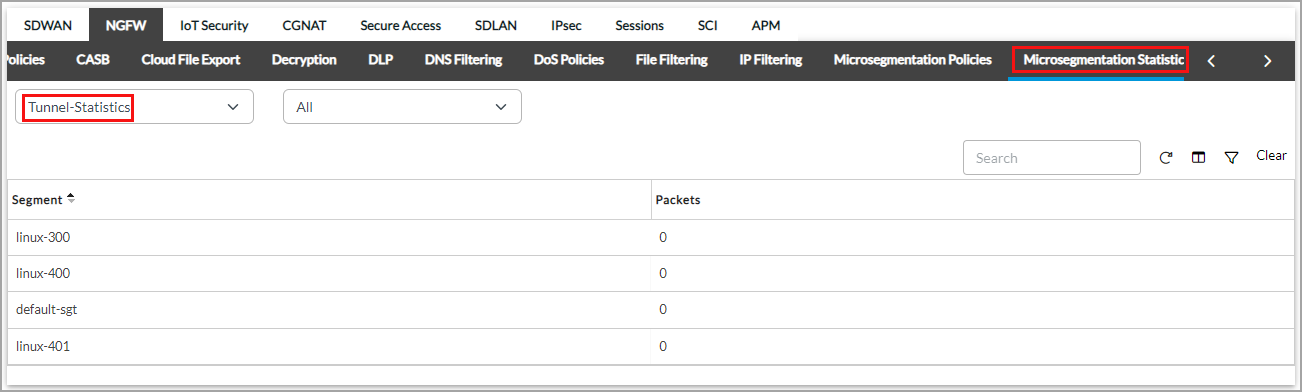
- To view brief microsegment statistics, select Brief.

Supported Software Information
Releases 22.1.3 and later support all content described in this article.
